Flexible PCB material
By:PCBBUY 08/02/2021 09:13
Flexible circuits are members of electronic and interconnection family. They consist of a thin insulating polymer film having conductive circuit patterns affixed thereto and typically supplied with a thin polymer coating to protect the conductor circuits. The technology has been used for interconnecting electronic devices since the 1950s in one form or another. It is now one of the most important interconnection technologies in use for the manufacture of many of today's most advanced electronic products.
In this passage, we will tell you everything about basic material flexible PCB. Please check and read the content we prepare below to learn more information.
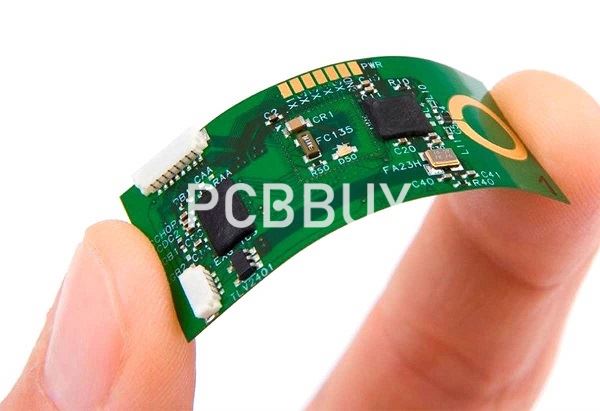

What is the substrate material improvement?
The functions of film substrate material lie in its capability to provide conductor carrier and insulating medium between circuits. Moreover, it has to be able to be bent and curled.
Usually-applied substrate material for flexible PCB includes PI (polyimide) film and PET (polyester) film apart from which polymer film is also available like PEN (polyethylene nphthalate), PTFE and Aramid etc. Substrate materials film should be picked up based on their performance and cost.
The leading substrate material for flexible copper clad laminate (FCCL) covers PI, a type of thermosetting resin that won't reach a temperature to become softened or be able to flow. However, it can still maintain flexibility and elasticity after thermal polymerization, which is different from majority of thermosetting resin. PI features high thermal resistance and excellent electrical characteristics. However, PI leads to high humidity absorption and bad tear strength, which should be improved. Upgraded PI film features humidity absorption of 0.7% which is much lower than ordinary rate that is 1.6% and features higher dimensional stability, converting from ±0.04% to ±0.02%.
Both flexible CCL and rigid CCL call for environmental requirement that is halogen free, which is an inevitable and stringent trend of electronics industry. Based on regulations released by EU (Europe Union) and lots of countries, 6 types of hazardous substances are forbidden to be available in electronic devices since July, 2006 and PCBs including flexible PCBs mustn't contain brominated flame retardant.
PET resin features agreeable mechanical and electrical performance and its biggest disadvantage is bad heat resistance, leading it to be incapable of direct soldering and assembly. Performance of PEN is better than that of PET and worse than that of PI so that the applications of PEN keep going up.

In the world, categories of applicable plastic film exceed 2000 among which there must be some types suitable for flexible PCB fabrication. Thus, as applications of flexible PCBs become expanded, new flexible PCB substrate material will be applied.
Adhesive plays a role in bonding copper foil and substrate material film and its ordinary classifications cover PI resin, PET resin, modified epoxy resin and acrylic resin among which modified epoxy resin and acrylic resin are more used owing to their high adhesive force.
What is two-layer PI substrate material?
Flexible CCL usually contains three layers: polyimide, adhesive and copper foil. Since adhesive tends to reduce flexible PCB performance, especially electrical performance and dimensional stability, two-layer flexible CCL (2L-FCCL) without adhesive is developed. In addition, because 2L-FCCL doesn't contain adhesive that might contain halogen, it's good for environmental protection and is capable of meeting the demand of lead-free soldering by improving temperature from 220°C to 260°C to 300°C. Performance comparison between 2L-FCCL with no adhesive.
Three types of manufacturing methods of 2L-FCCL are available:
• Electroplating
• Film coating
• Lamination
By comparing three methods, it can be concluded that deposited electroplating metal layer on polyimide film is easy to be produced in rolling and thinner substrate material and copper foil can be picked up with low cost. Film coating is applicable for mass-volume production with a low cost. Lamination works better on double-side board fabrication.
What is LCP substrate material?
To essentially modify disadvantage of polyimide substrate material, liquid crystal polymer (LCP) is newly developed. As thermoplastic LCP film is covered with copper foil, which then receives constant hot pressing, single-side or double-side CCL will be obtained. This type of CCL features a water absorption rate that is only 0.04% and dielectric constant that is 2.85 (1GHz), compatible with demands of high-frequency digital circuits.
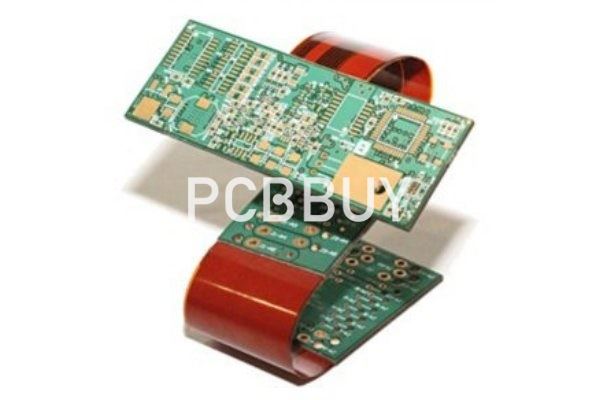

Polymer features a liquid state and it will be melted into hot melting liquid crystal polymer (TLCP). When it comes to merits of TLCP, it can be molded through injection and fabricated by pressing into thin film that will be substrate material for PCB and flexible PCB. Moreover, it is capable of going through secondary processing, recycled and reused. Owing to low humidity absorption, high-frequency suitability and thermal dimensional stability of TLCP, it starts being applied in flexible PCB.
What is new copper foil?
Leading conducting material of flexible PCB is copper or copper foil and sometimes alloy is also used including aluminum, nickel, gold and silver etc. Apart from conduction, conductor layer should be flexibility resistant. In accordance with different manufacturing methods, copper foil is classified into electro deposit (ED) copper foil and rolled and annealed (RA) copper foil. Difference between the two types of copper foil lies in different crystal shapes: RA copper foil features a column array shape, leading to even and flat structure, accessible to roughening and etching processing. ED copper foil features fish scale, leading to smooth copper foil with good toughness, but inaccessible to roughening or etching processing. As far as dynamically flexible PCB is concerned calling for high flexibility, RA copper foil is usually applied.
Currently, high-density flexible PCB mainly depends on ED copper foil. To be able to compatible with requirement of mass-volume production of PCB whose pitch is within the range from 40μm to 50μm, new demands are laid. One is that copper foil surface should receive low roughness and the other is that copper foil should be ultra thin.
Industry Category











