For Beginners: Top 7 Essential Tips of PCB Trace Spacing Standard
By:PCBBUY 11/24/2021 09:21
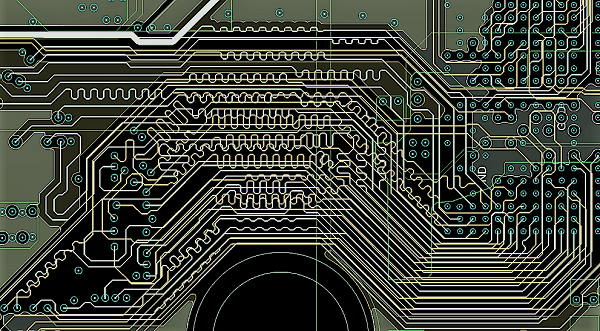
For digital designs with high speed communication, specific spacing and tuned lengths may be required to minimize cross-talk, coupling, and reflections. Some common applications for this are USB-based serial differential signals, and RAM-based parallel differential signals. Generally, USB 2.0 will require differential pair routing at speeds of 480Mbit/s (USB high speed class) or higher. This is partly because high-speed USB generally operates at a much lower voltage and differential, bringing the overall signal level closer to the noise floor.
For the beginners of PCB industry, are you searching for more information about the PCB trace spacing? If you are going to learn more about PCB trace spacing, please check and read the content in this passage for more information.

What is the PCB trace clearance?
High voltage/high current designs carry safety requirements which need to be met by designers. Similarly, high speed designs need to have suppressed crosstalk in order to ensure signal integrity. The key design aspects that relate to both areas are your PCB trace clearance and pad clearance values. These design choices are critical for balancing safety, noise suppression, and manufacturability.
The IPC 2221 standards provide guidance for preventing ESD between conductors, but not all boards will need to meet this standard. Depending on the voltage and frequency of your signals (or edge rate for digital signals), you may need a different value for your PCB trace clearance. Here’s how to balance these two aspects of your PCB layout while also ensuring manufacturability.
How to determine PCB trace width?
These trace width calculators will prompt you to enter design specifications such as the thickness of copper, the maximum amperage that will pass through the trace, the length of the trace, and the acceptable increase in temperature due to the resistance of the trace dissipating power. After entering these values you will be presented with a calculated trace width. It is important to note that this value is a minimum width required to meet the design criteria inputs.

Now, a PCB trace acts as a resistor and the longer and narrower the trace, the more resistance is added. If we assume some general things like a 1-ounce copper pour and ambient room-temperature during normal operation, we have what we need to calculate both the minimum trace width and expected voltage drop at that width.
Trace Spacing
The size of a PCB is directly connected to the cost of the PCB, so in general PCBs are kept as small as possible. The downside of reducing board size is that it can limit the available space to route traces. For low power signal traces it is generally advised to keep traces small to increase the available space available for routing. Excessively large traces consume valuable PCB space while offering highly diminished returns. 6 to 30 mils is typical for most signal trace widths.
How to process standard PCB trace spacing?
PCB trace widths and spacings can affect the circuit board in many ways. Here are four areas to consider when deciding what width and spacing values to use:
Electrical Performance and Signal Integrity
Most digital routing on a circuit board will use a default value for its trace widths and spacings, but some nets will require different sizes. Controlled impedance nets, for instance, will need their trace widths calculated based on the configuration of the board layer stackup. Sensitive high-speed traces may require larger spacing values to prevent crosstalk and other signal integrity problems.
Analog routing may also require unique trace widths and spacings depending on the purpose of the circuitry. In some cases, the default trace width may be reduced in tight and constricted areas, but care has to be taken that this isn’t extended across the board. If the trace gets so thin that it gets compromised during PCB fabrication, then the signal integrity of the entire board could be compromised.
Power and Ground Routing
Traces used to route power and ground need to be wider to conduct greater amounts of current. If the traces are too thin, they can get hot and even burn through. Power traces routed on the internal layers of the board also need to be wider for heat dispersal than those routed on the external layers, as exposure to the air will provide more cooling. For those traces that are used in power supply circuitry, it is important to keep them as short and as wide as possible to handle the current, as well as to reduce inductance and noise in the circuit. It is important to increase the spacing for traces that are carrying higher current to prevent the power from arcing between them.
How to determine standard PCB trace width?
Let's walk through the process of calculating for a certain trace width for a power signal delivering current from one power component to a peripheral. In this example, we’ll be calculating the minimum trace width for a power-path used for a DC motor. The power-path starts at a fuse, travels through an H-bridge (a component used to manage power delivery across a DC’s motor windings), and ends at the motor’s connector. The average continuous max current demanded by the DC motor will be around 2 Amps.
Now, a PCB trace acts as a resistor and the longer and narrower the trace, the more resistance is added. If the trace isn’t properly defined, the high current could damage the trace and/or introduce significant voltage drop to the motor (resulting in a slower speed). NetC21_2 shown in Figure 3 is about 0.8” long and needs to carry 2 Amps max. If we assume some general things like a 1-ounce copper pour and ambient room-temperature during normal operation, we have what we need to calculate both the minimum trace width and expected voltage drop at that width.
Industry Category











