How to Choose PCB Material of PCB Design Process Tutorial?
By:PCBBUY 10/09/2021 09:33
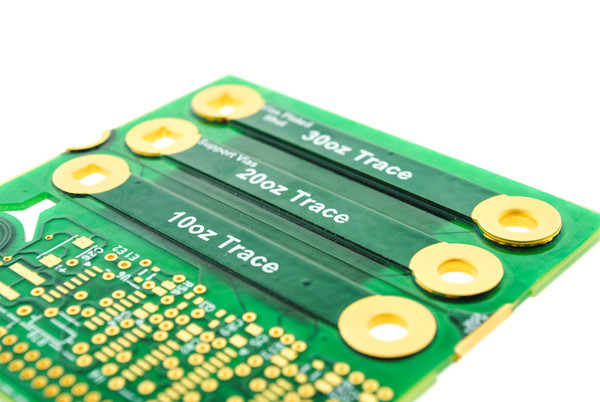
PCB may use a variety of materials as substrates and components. Material selection depends on the requirements of the application, as different material choices will give the circuits varying qualities that facilitate performance in specific circumstances.
Designers sometimes choose materials based on electrical performance for high speed applications, or mechanical or thermal survivability – for example automotive under the hood applications. Designers may choose to comply with regulatory governmental requirements. For example, the European Union’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive forbids the use of materials containing any restricted chemicals and metals.
In this passage, we will focus on the methods of choosing the correct the material for PCB. Check and read the content for more professional information.
What are the 3 main types of PCB material?
There are three major types of materials used for fabrication of PCBs:
FR-4
This is the most commonly used material in PCBs. It is a glass reinforced epoxy laminate sheet. The epoxy used is flame retardant and water resistant. It provides good strength to weight ratios. The tensile strength offered by this material is very high.
PTFE (Teflon)
PTFE is a kind of plastic material that does not provide any resistance, thus is used for high speed, high frequency applications. PTFE is extremely flexible, making it invaluable in applications with tight tolerances. It is also extremely lightweight, allowing it to be used across various industries. It is also flame resistant, exhibits high physical strength, provides temperature stability, and is versatile in application.
Metal
The traditional materials of copper, aluminum, iron, etc. are still used in PCBs. These materials allow the use of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for the integration of components. They also provide mechanical durability. Thus, the product life of metal base PCBs is much longer.
The different materials used for the PCB design and fabrication, all offer a variety of advantages and disadvantages. The material is chosen according to the application, the result needed, environmental factors, and any other constraints the PCB will face. You should choose the material of the PCB depending on the results that are expected.
How to choose the correct material for PCB?
When you choose the PCB materials, you need to take quality into consideration that is quite important in your board, because it can offer superior performance for the full duration of PCB’s expected lifespan. So you can choose the PCB materials based on your demands.
When to choose standard FR-4?
Save product costs and is affordable and effective for many applications.
When to choose Rogers materials?
if you need dielectric PCB properties in your boards, rogers materials is a good choice with higher performance and electrical properties, especially the power management, such as high speed designs, RF, microwave, or mobile applications.
When to choose metal core?
if you are making a electronic project of LED based products, choose the metal core in your boards. What’s more, metal core PCB is more and more common in a variety of lighting applications-for home, workplace, and vehicle.
When to choose HDI material?
HDI technology is a good solution for smaller and lighter products, high-tech applications, denser BGA and QFP packages, as well as lowered heat transfer included stress.
When to choose high Tg?
If there is a higher power density in electronic products and heat generation will tend to disturbing heat sink or other parts of the products, so high Tg PCB is the best solution. What is more, you can find that high Tg PCBs are applied in electronic industries which can operate in relatively high temperatures as high Tg PCB are more and more popular in recent years.
What is the future of PCB material?
While minor changes in the ink used for silkscreen or the materials in your soldermas aren’t likely to make any headlines, the bulk of innovation effort seems to be focused on improving the CCL.
· The need for smaller, lighter boards for applications such as mobile devices has increased the demand for multilayer architectures which can pack more functionality into a smaller form factor.
· Enhanced epoxy systems such as Getek, Megtron, 4000-13 and FR-408, which cite better performance than FR-4 with reduced Dk values and loss tangents.
· High performance materials such as A-PPE by Asahi Glass, Nelco 600-21 Si, and Rogers 4350, which offer significant improvements in lower Dk, better impedance control, and reduced jitter.
· Flexible CCLs made of PI or polyester.
· Stricter RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) regulations have encouraged higher heat resistance and reliability. Halogen-free CCLs limit chlorine and bromine content to within 900 ppm. Lead-free CCLs remove lead by swapping the DICY curing system of standard FR-4’s with a PN curing system using phenol-formaldehyde resin curing agent.
Industry Category











