How to Choose a PCB SMT Factory: A Comprehensive Guide for Engineers & Buyers
By:PCBBUY 05/27/2025 15:19
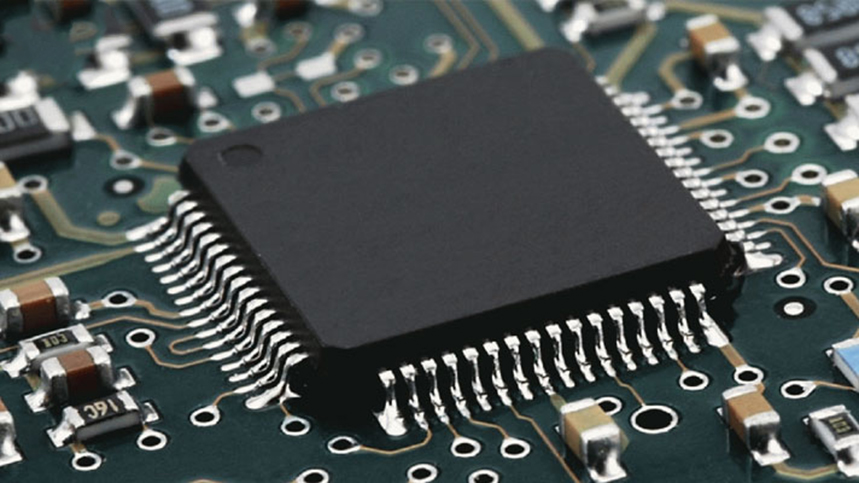
1. Understanding SMT Fundamentals: Technology Overview
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is the backbone of modern electronics manufacturing, involving the automated placement of components on printed circuit boards (PCBs) and soldering processes. Unlike through-hole techniques, SMT enables higher component density, miniaturization, and faster production cycles. However, the complexity of SMT requires rigorous control over equipment calibration, material properties, and process parameters.
Critical SMT Process Steps:
-
Solder Paste Screening: Precise stencil alignment and paste deposition.
-
Component Placement: High-speed pick-and-place machines install parts with micron-level accuracy.
-
Reflow Soldering: Thermal profiling to melt solder without damaging components.
-
Inspection: Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray imaging for defect detection.

Key Technical Parameters:
-
Placement Accuracy: Typically ±0.05 mm for consumer electronics, ±0.025 mm for automotive/medical devices.
-
Soldering Profiles: Reflow ovens must maintain ±5°C tolerance in peak temperatures (e.g., 245°C ±5°C for lead-free solder).
-
Component Mix: Capability to handle 0201, 01005 passives, and fine-pitch BGAs (e.g., 0.4 mm pitch or lower).
2. Equipment Capabilities: The Backbone of SMT Precision
The reliability of SMT output depends on the factory’s equipment fleet. Critical equipment categories include:
|
Equipment Type |
Key Brands |
Technology Benchmarks |
|
Pick-and-Place Machines |
Fuji, ASM, Juki, Yamaha |
±0.03 mm placement accuracy, 150,000+ CPH (components per hour) |
|
Reflow Ovens |
Heller, BTU, Vitronics |
±0.1°C temperature uniformity, 14-zone convection control |
|
AOI Systems |
Viscom, Omron, Konica Minolta |
25-micron resolution, 99.9% defect catch rate |
|
X-ray Inspection |
Nikon, YXLON |
1-micron resolution for detecting BGA solder voids |
Why Equipment Matters:
-
Throughput: Factories with high-speed lines (e.g., 0.08 seconds per component) reduce labor costs.
-
Precision: Older machines (>10 years) may lack the calibration for modern 01005 components.
-
Data Integration: Advanced factories use MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) for real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control) tracking.

3. Quality Assurance: Beyond AOI and X-ray
A robust quality system combines equipment, personnel, and processes. Look for:
3.1 Certifications & Standards
|
Certification |
Relevance to SMT |
|
IPC-A-610 |
Acceptable solder joint standards (Class 1: General electronics; Class 3: Aerospace/medical) |
|
IATF 16949 |
Automotive-specific quality management (mandatory for automotive SMT suppliers) |
|
ISO 13485 |
Medical device manufacturing compliance |
|
RoHS/REACH |
Compliance with hazardous substance restrictions |
3.2 Defect Rate Benchmarks
|
Defect Type |
Consumer Electronics |
Automotive |
Medical Devices |
|
Solder Joint Opens |
<50 ppm |
<10 ppm |
<5 ppm |
|
Misaligned Components |
<30 ppm |
<5 ppm |
<2 ppm |
|
Cold Solder |
<20 ppm |
<3 ppm |
<1 ppm |
Note: PPM = Parts Per Million; automotive/medical require IPC Class 3 standards.
4. Cost Analysis: Balancing Price and Performance
While cost is a critical factor, cheaper options often compromise quality. Key considerations:
4.1 Direct Costs
-
Per-unit pricing: Varies by volume (e.g., 0.01–0.01–0.05/cm² for low-volume, 0.001–0.001–0.005/cm² for high-volume).
-
Setup Fees: Negotiate for first-time setup costs (e.g., 500–500–2000 per project).
-
Tooling: Custom stencils or trays may add 100–100–500 per revision.
4.2 Hidden Costs
-
Rework Rates: Factories with >1% rework increase costs by 10–20%.
-
Lead Time Penalties: Missed deadlines can cost 500–500–5000/day in urgent projects.
-
Warranty Claims: Defective batches may incur return shipping and testing expenses.
Cost-Optimization Tips:
-
Request a cost breakdown (materials, labor, overhead).
-
Compare total cost of ownership (TCO) over 3–5 years for long-term partnerships.

5. Supplier Audit: A Checklist for Due Diligence
Perform a multi-step audit to validate capabilities:
5.1 Technical Assessment
-
Equipment Age: Ensure <5% of machines are >10 years old.
-
Calibration Records: Daily checks for pick-and-place accuracy and reflow profiling.
-
First Pass Yield (FPY): Target >98% for consumer electronics, >99.5% for automotive.
5.2 Production Capacity
|
Factory Size |
Monthly Capacity |
Flexibility |
|
Tier 1 (Foxconn, etc.) |
500,000+ panels/month |
Low (prioritizes large OEMs) |
|
Mid-tier (regional) |
50,000–200,000 panels/month |
Medium (handles mid-volume orders) |
|
Small boutique |
<20,000 panels/month |
High (customized rapid prototyping) |
5.3 Environmental & Ethical Compliance
-
Conflict Minerals Policy: Ensure adherence to CSR initiatives (e.g., RMI certification).
-
Waste Management: Solvent recycling rates >95% for environmental sustainability.

6. Long-Term Partnership Strategies
A reliable SMT partner should evolve with your needs:
6.1 Technology Roadmap Alignment
-
Component Roadmap: Support for emerging packages (e.g., fan-out wafer level packaging, FoWLP).
-
Green Manufacturing: Lead-free solder, halogen-free laminates, and REACH compliance.
6.2 Risk Mitigation
-
Geographic Redundancy: Dual sourcing from regions with political/economic stability.
-
Inventory Safety Net: Partners with component stocking programs reduce lead times.
6.3 Intellectual Property Protection
-
NDAs: Mandatory for custom designs.
-
Secure Data Handling: ISO 27001-certified IT systems for design files.
7. Case Study: Automotive vs. Medical SMT Requirements
|
Application |
Key Differentiators |
|
Automotive (ADAS) |
-25°C to +125°C operating range; IPC-610 Class 3 solder joints |
|
Medical (MRI) |
Biocompatible materials; <1 rad magnetic resonance interference |
|
Consumer (IoT) |
Cost-optimized processes; rapid prototyping flexibility |
Conclusion: A Weighted Scoring Framework
Use the following criteria to prioritize vendors:
|
Criterion |
Weight |
Score |
Notes |
|
Equipment Precision |
25% |
Based on machine specs and maintenance records |
|
|
Quality Compliance |
20% |
IPC class, defect rates |
|
|
Cost Transparency |
15% |
TCO vs. per-unit pricing |
|
|
Supply Chain Resilience |
15% |
Geographic diversity, inventory policies |
|
|
Innovation Capacity |
15% |
R&D investment, new technology adoption |
|
|
Total Score |
100% |
Weighted sum for final ranking |
References
-
IPC Association. IPC Standards Handbook. IPC.org.
-
Fraunhofer Institute. Advanced SMT Process Technologies. Springer, 2023.
-
Grand View Research. Global SMT Market Report. Q1 2024 Edition.
-
Heller Group. Thermal Profiling Best Practices. Whitepaper, 2022.
-
JEDEC Standards. Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Testing. JEP143B.
Industry Category











