How to Design Flexible PCB with 5 Important Aspects?
By:PCBBUY 11/05/2021 09:57
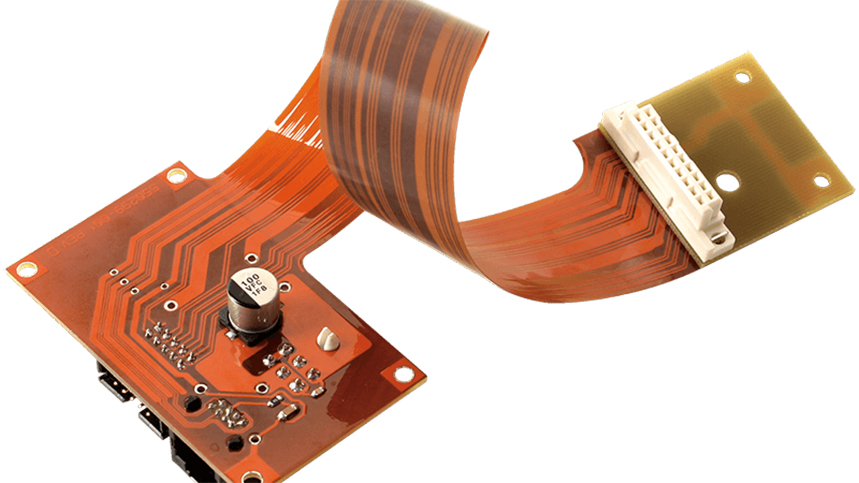
Flex PCB prototypes aren’t new in electronics, with the earliest description filed in a patent in the early 1900s. In modern electronics, you’ll find flex circuits in keyboards, smart watches, mobile phones, printers, and other industrial applications. With the recent trend of electronics getting smaller, the demands for flex PCB prototype design has increased.
Are you going to learn more about flexible PCB? You can check and read the content we prepare for more professional knowledge.

1. What is the basic information of flexible PCB?
It is vital to know two things about flexibility: how many times the PCB will be flexing, and to what extent the PCB will flex. The amount of times it can bend, or application, determines whether the board will be a static or dynamic board. A static board is considered bend-to-install and will flex less than 100 times in its lifetime. A dynamic board’s design needs to be more robust in nature, as flexing will be done on a regular basis—and will need to withstand tens of thousands of bends. These PCBs are used in very harsh conditions such as spacecraft and military applications.
To know more about military-grade PCB specifications, read our article: Military-Grade PCB Design Rules and Considerations. Bend radius—the minimum amount of bendiness for the flex area—must be properly identified early in the design. This ensures your design can allow for the necessary number of bends without damaging the copper. The figure below will help determine how thick you can make your circuit.
2. How to determine the material for flexible PCB?
Polyimide flex cores are cladded with either electro-deposited or rolled annealed copper. This copper is very thin and is suitable for both dynamic and static applications. 0.5oz (0.7mils) copper is commonly used in flex PCBs. The most common flex PCB copper weights are 0.5oz and 1oz. The maximum copper weight is 2oz. This gives the best combination of the thinnest possible construction.
There are two major types of flex materials:
· Adhesive-based where the copper is bonded to the polyimide with acrylic adhesive.
· Adhesive-less where the copper is cast directly onto the polyimide.
3. What are the advantages of flexible PCB?
Flex circuits offer numerous benefits that make them ideally suited for designs where saving weight and space and incorporating complex design movement are critical. These benefits include:

Repeatable reliability
A flex circuit allows you to customize a routing path within your printed circuit board, which provides enhanced reliability and dependability.
Withstands tough environments
The materials used ensure that flex circuits can withstand a full spectrum of gravitational force, and taxing conditions — from dropping your cell phone to the launch of a missile.
Survives high temperatures
Flex circuits are able to endure higher temperatures, which makes them ideal for a wide variety of industries, including aerospace, military, down hole oil, and medical.
Long-duty cycles
A flex circuit’s durability means it can tolerate a large volume of flexing cycles while carrying signal and power without disruption.
High vibration
Flex circuits have low mass and are ductile, which means they can undergo a significant strain or shape change without breaking or losing strength. As a result, flex circuits can withstand high vibrations.
4. What is HDI flexible PCB?
The HDI stands for high-density interconnect. These circuit designs are efficient, reliable and come with better design, construction, and layout compared to other boards. HDI flexible boards offer better electrical performance and reduced package size due to the thinner substrate material used for the manufacturing of these boards.

5. What are the applications of flexible PCB?
FPCBs are used widely in everyday technology and electronics in addition to high-end, complex completed components. A few of the most prominent examples of flexible circuits usage is in modern portable electronics, devices, hard disk drives and desktop printers.
Flexible circuits are also used extensively in other applications and industries including:
· Communications
· Consumer Electronics
· Automotive
· Medical
· Industrial
· Aerospace
· Military
· Transportation
Industry Category











