How to Process PCB First Article Inspection?
By:PCBBUY 07/31/2024 16:18
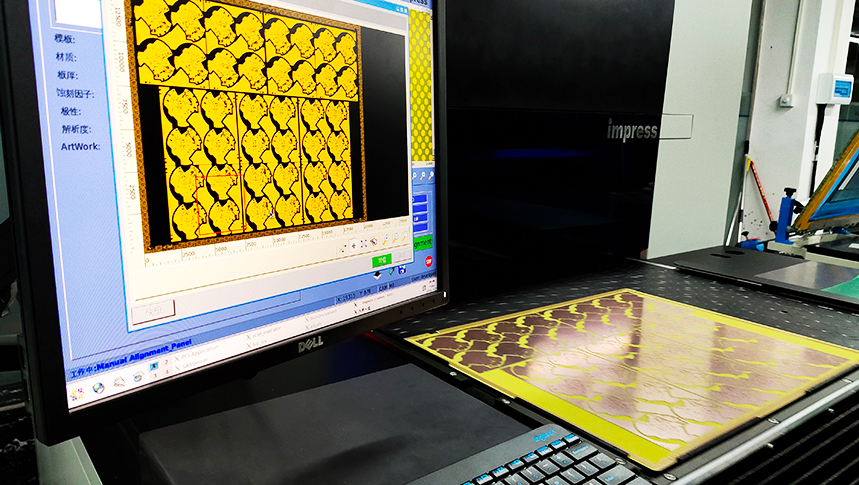
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing is a complex process that requires precise control and verification to ensure the final product meets the necessary quality and performance standards. First Article Inspection (FAI) is a critical step in this process, providing a detailed assessment of a PCB's conformity to design specifications before mass production. This article explores the FAI process for PCBs, detailing its significance, methodologies, and best practices. It includes industry knowledge, data support, equations, and tables to provide a comprehensive understanding.
What is First Article Inspection?
First Article Inspection (FAI) is a formalized process of validating a manufactured part or assembly against design specifications. In the context of PCB manufacturing, FAI involves a thorough inspection and testing of the first produced PCB to ensure it meets all design and manufacturing requirements. This inspection is crucial for:
Identifying defects early in the production process
Validating manufacturing processes and materials
Ensuring compliance with design specifications and standards
What Is the Importance of FAI in PCB Manufacturing?
FAI plays a vital role in the quality assurance process by:
Preventing costly mass production of defective boards
Ensuring that all design and production standards are met
Providing a benchmark for future production runs
Facilitating communication and understanding between manufacturers and clients
What Are the Key Components of PCB FAI?
Documentation and Preparation
1. FAI Checklist
An FAI checklist outlines all the parameters and features that need to be inspected. This checklist is based on the design documentation, including the Bill of Materials (BOM), Gerber files, and assembly drawings.
2. Control Plan
A control plan details the inspection procedures, measurement techniques, and equipment to be used during FAI. It ensures consistency and accuracy in the inspection process.
Inspection Criteria
1. Dimensional Verification
The dimensional accuracy of the PCB is checked against the design specifications. This includes the overall dimensions, hole sizes, pad spacing, and component placements.
2. Material and Component Verification
Verification of materials involves checking the substrate, copper layers, solder mask, and surface finish. Components are inspected to ensure they match the specifications in the BOM.
3. Soldering and Assembly Quality
The quality of solder joints, component orientation, and assembly workmanship are inspected. This includes checking for defects such as solder bridges, cold joints, and misaligned components.

What Is the Detailed FAI Process for PCB?
Step 1: Pre-Inspection Preparation
Review of Design Documentation
Before the FAI begins, all relevant design documents are reviewed. This includes:
Gerber Files: Detailed representations of each PCB layer, used for manufacturing.
BOM: A comprehensive list of components required for the PCB, including part numbers, descriptions, and quantities.
Assembly Drawings: Diagrams showing the placement of components on the PCB.
|
Document Type |
Purpose |
|
Gerber Files |
Layer specifications |
|
Bill of Materials |
Component list |
|
Assembly Drawings |
Component placement guidance |
Preparation of Inspection Tools and Equipment
The appropriate tools and equipment for FAI are prepared, including:
Micrometers and Calipers: For measuring dimensions.
Optical Inspection Systems: For detailed visual inspection.
Multimeters and Test Jigs: For electrical testing.
Step 2: Visual Inspection
Surface and Finish Quality
The surface of the PCB is inspected for:
Solder Mask: Checking for uniform coverage, thickness, and defects.
Surface Finish: Verification of the type and quality of the finish, such as HASL, ENIG, or OSP.

Component Placement and Soldering
The inspection includes:
Component Orientation: Ensuring correct placement and orientation according to the assembly drawings.
Solder Joint Quality: Inspecting for adequate solder coverage, wetting, and joint strength.
|
Inspection Aspect |
Criteria |
|
Criteria |
Coverage, thickness, defects |
|
Component Placement |
Accuracy, orientation |
|
Solder Joint Inspection |
Coverage, wetting, joint integrity |
Step 3: Dimensional Verification
Measurement of PCB Dimensions
Key dimensions such as board thickness, hole sizes, and pad spacing are measured and compared with the design specifications.
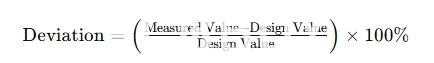
Hole and Pad Size Verification
Measurement of hole diameters and pad sizes ensures that they meet tolerances specified in the design documents.
|
Dimension |
Tolerance (%) |
Measured Value |
Design Value |
Deviation (%) |
|
Board Thickness |
±10% |
1.60 mm |
1.50 mm |
+6.67% |
|
Hole Diameter |
±5% |
0.20 mm |
0.21 mm |
-4.76% |
|
Pad Size |
±2% |
1.00 mm |
1.02 mm |
-1.96% |
Step 4: Electrical Testing
Continuity and Isolation Testing
Continuity Testing: Ensures that electrical connections are intact.
Isolation Testing: Verifies that there are no unintended connections between different circuits.
|
Test Type |
Criteria |
Result |
|
Continuity |
All connections must pass |
Pass/Fail |
|
Isolation |
No shorts between traces |
Pass/Fail |
Functional Testing
Functional Test: Verifies the PCB’s functionality by simulating operating conditions.
Power-Up Test: Ensures that the PCB can power up and operate as intended without issues.

Step 5: Documentation and Reporting
FAI Report
An FAI report documents all inspection results, including:
Visual Inspection Findings
Dimensional Measurement Results
Electrical Test Outcomes
Any Deviations or Non-Conformities
Non-Conformance Reporting
If any discrepancies or defects are found, they are documented, and corrective actions are proposed. This may include process adjustments or design changes.
Best Practices for Effective FAI
Continuous Improvement
FAI should be part of a continuous improvement process, where feedback from FAI results is used to enhance design, materials, and processes.
Training and Skills Development
Ensure that personnel conducting FAI are adequately trained and familiar with the latest standards and inspection technologies.
Use of Advanced Inspection Technologies
Incorporate advanced inspection tools such as automated optical inspection (AOI) systems, X-ray inspection, and 3D measurement systems to enhance accuracy and efficiency.

Conclusion
First Article Inspection (FAI) is an essential process in PCB manufacturing, ensuring that the first produced boards meet all specified requirements before mass production. By following a structured FAI process, manufacturers can identify and correct defects early, improve product quality, and ensure customer satisfaction. The adoption of best practices, continuous improvement, and advanced inspection technologies further enhances the effectiveness of FAI.
References
1. IPC-A-600, "Acceptability of Printed Boards," IPC, 2019.
2. IPC-6012, "Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards," IPC, 2020.
3. J. H. Lau, "Advanced Soldering Techniques," McGraw-Hill, 2002.
4. C. F. Coombs, "Printed Circuits Handbook," 7th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2016.
5. K. Gilleo, "Area Array Packaging Handbook: Manufacturing and Assembly," McGraw-Hill, 2002.
Industry Category











