How to Protect Copper Traces on Outer Layer of PCB from Corrosion?
By:PCBBUY 04/19/2022 09:48
Environmental factors that normally affect a PCB are temperature, chemical attack, physical shock (vibration) and thermal shock; the trick is to decide which of these is likely to have the greatest impact upon your PCB and then concentrate on making an appropriate resin choice. Each of the three main resin types (epoxy, polyurethane and silicone) has its strong points, as well as weaknesses.
If you are looking for the knowledge of PCB copper, you can check and read this passage for more information about PCB copper. Don’t miss the useful content for your PCB area to study. Let’s check it!
What is electrochemical corrosion failure?
There are two primary electrochemical corrosion mechanisms: galvanic and electrolytic. Galvanic corrosion occurs when two different metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an ionic contamination or an electrolyte solution. There is a natural voltage difference between the two metals (known as the “electrode potential”). As a result, current flows towards the more resistant metal, and the more resistant metal corrodes faster.
This type of corrosion typically occurs at electrical connections between components and traces. PCB corrosion begins once moisture or some other liquid comes into contact with the electrical connection. PCBs in industrial environments, humid environments, or other extreme environments are highly susceptible to this form of corrosion.
Electrolytic corrosion occurs when neighboring traces become contaminated by an ionic liquid or electrolytic solution. Small slivers begin to grow between the two traces. If the contaminant is water, metal oxides and hydroxides will start to grow on the exposed metal.
If two neighboring traces in a circuit board are close to each other, there is a chance that the slivers bridge the two traces, causing a short. This short circuit can disable a particular functional block in your PCB. If corrosion occurs between nearby power and ground lines, it could disable the entire device.
Aside from a neighboring copper trace, copper that is adjacent a surface ground plane can corrode when exposed to ionic or environmental contamination. In the presence of halogens, copper converts into copper halide compounds as halogen gases interact with the surface of exposed copper, causing tiny pits to accumulate over time. After soldering, any exposed copper should be cleaned and coated to prevent corrosion if the circuit board will be in an environment where it may be exposed to halogens.
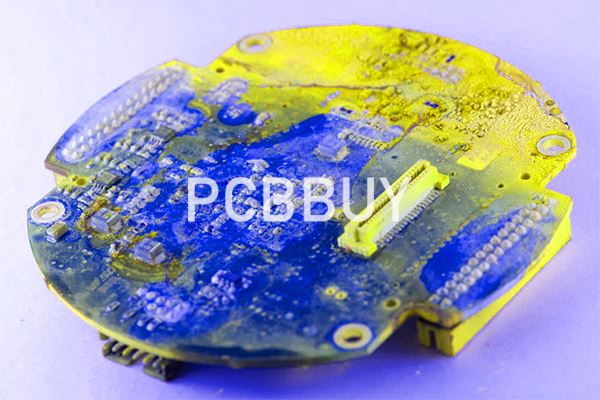

How to prevent corrosion of PCB trace?
From the above, it is clear that corrosion is primarily due to the presence of moisture or electrolytic contaminants on the PCB. Extreme environments such as industrial and humid atmosphere are liable to make PCBs highly susceptible to different types of corrosion. Preventing corrosion is possible by:
· Removing flux residues effectively from the PCB
· Keeping the PCB dry
· Preventing electrolytes from wetting the PCB
· Covering the PCB with a conformal coating
Older flux materials were notorious for generating chlorine or other harmful halogens, which led to formation of pitting corrosion in copper traces, unless the flux material was removed after the soldering process. However, organic acids in newer fluxes do not contain halogens, and they decompose at higher temperatures such as during reflow soldering. However, boards undergoing wave soldering may not reach the decomposing temperature, and the leftover flux residue may have to be manually cleaned thoroughly to prevent crevice corrosion.
It is largely possible to win the war against corrosion by preventing moisture or other liquids from reaching the PCB. There are many ways to achieve this, such as by placing the PCB inside an enclosure with a suitable IP rating.
In situations where it is not possible to enclose the PCB in an enclosure, conformal coatings can help. Different forms of conformal coatings, such as a simple solder mask, aerosol spray coatings, or epoxy coatings are all effective deterrents against corrosion. However, for PCBs carrying components that generate heat, such conformal coatings may have to be applied judiciously so as not to hamper heat management.
Industry Category











