How to Protect PCB from Corrosion with 5 Efficient Tips?
By:PCBBUY 10/14/2021 09:28

Can anyone suggest some tips and tricks for making PCBs more corrosion resistant? Sometimes, moisture gets into the enclosures. I've noticed that solder joints can start to corrode, and recently moisture made it under the solder mask on a board and actually ate through one of the traces, breaking the circuit.
If you are going to provide you everything about PCB corrosion, please check and read the content below for more information. Let’s go for the tips of preventing PCB corrosion.
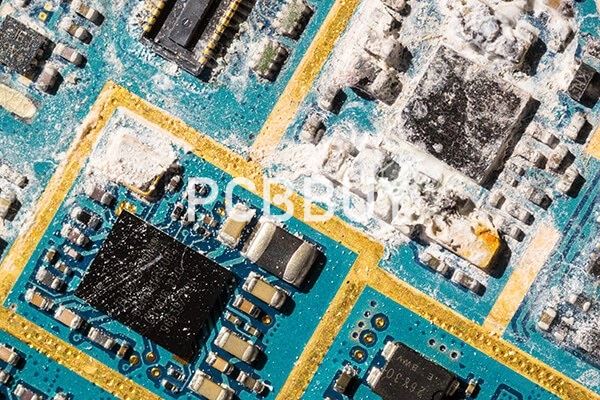

1. What are the types of PCB corrosion?
Of the above, metal on PCBs are more likely to face the first five types of corruption as discussed below:
General attack corrosion
Also known as atmospheric corrosion or uniform attack corrosion, this is the most common type of corrosion. Caused mostly by a chemical reaction between the oxygen in the atmospheric moisture and copper, the result is the formation of copper oxide.
Localized corrosion
Unlike general attack corrosion that affects a larger area, localized corrosion is limited to a small area and may be of one of three types:
· Filiform Corrosion: Moisture entering under the surface finish causes a tiny defect in the copper, which then spreads further.
· Crevice Corrosion: Stagnant micro-environments such as those under clamps, washers, and components on PCBs cause this type of localized corrosion. Left-over flux and cleaning solution within such crevices commonly cause this type of corrosion.
Galvanic corrosion
In the presence of a corrosive electrolyte, two dissimilar metals, such as copper and the metal cap of an SMD, or gold and tin, can start to corrode due to galvanic corrosion. Although similar to pitting corrosion, galvanic corrosion occurs only between electro-chemically dissimilar metals when they are in electrical contact, and the metals are both exposed to the electrolyte.
2. What are the causes of PCB corrosion?
Corrosion is the gradual breakdown of material, usually metal, by a chemical reaction with its environment. The most common form of corrosion occurs with you combine metal with water and oxygen, creating iron oxide (or what is more commonly known as rust). This reaction occurs when you combine these elements together for an extended period of time.
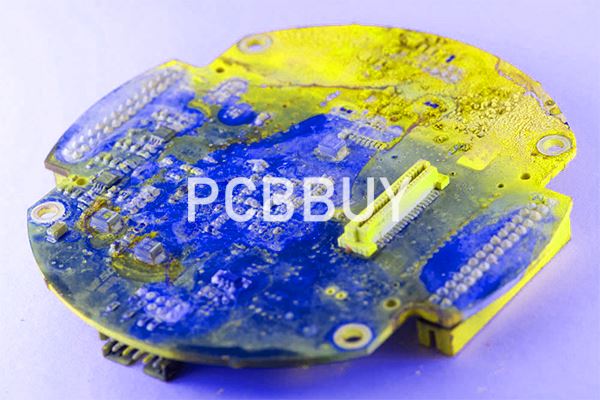

Two types of contaminants can cause corrosion and dirt on the printed circuit boards. These are:
· Dry contaminants: It is an obvious answer that dirt and debris will make the boards dirty most often or not. It accumulates through the air and easy to clean as well.
· Wet contaminants: Soda, waxy oil, grime, and flux are the wet contaminants and cause corrosion on the boards. It needs different cleaning and drying approaches to prevent permanent damage to the board and device.
3. How to remove PCB corrosion?
When the PCB receives water damage or other sources of corrosion, cleaning it can be an important way to repair it.
Washing Water
Washing water refers to chemical industrial cleaning agent potion used to clean the flux and rosin on the surface of PCB circuit board after soldering. The traditional method for cleaning printed circuit boards is to use organic solvents. A mixed organic solvent consisting of CFC-113 and a small amount of ethanol (or isopropanol) has a good ability to clean the residue of rosin flux, but because of CFC- 113 has a destructive effect on the atmospheric ozone layer and has been banned in 2013. The optional non-ODS cleaning processes include water-based cleaning, semi-water-based cleaning, and solvent cleaning.
Baking Soda
The alkalinity and abrasiveness of baking soda make it an ideal cleaner for PCB corrosion. It can effectively remove all corroded areas without causing any damage to the PCB itself.
4. What are the necessary tools for removing PCB corrosion?
When you are ready with the necessary chemical solutions for the corrosion removal procedure, next, you will need a proper removing tool for the board. It includes:
Microfiber cloth or rug:
You can use a small towel or piece of cloth to quickly wipe out the applied chemical such as isopropyl alcohol or baking soda from the board. However, make sure that the fabric you are using is lint-free, which will leave fewer residues on the board.
Paintbrush:
A small paintbrush with soft bristles will also work fine to remove the rust and corrosion from the board. The bristles need to be fragile so that it won’t leave any scratches on the board. Also, it is helpful to reach the tiny gaps on the board to get a full cleaning with ease.
A blow dryer or hairdryer:
Sometimes you may require drying the printed circuit board since the liquids won’t get away totally from the board. In this case, we thoroughly recommend you use a heat source such as hair or blow dryer for the purpose.
5. How to keep safe during removing PCB corrosion?
To avoid dirty circuit boards, you can take preventative steps. Get in the habit of ensuring any electronics not in use are set to the “OFF” position, as the likelihood of adverse repercussions resulting from water damage significantly drop if the affected areas dry before reactivation.
Exercise caution when handling circuit boards:
· Disconnect the device from its power source
· Avoid standing near any water
· Wear dry clothes
Industry Category











