How to Solder a Broken Wire on a Circuit Board?
By:PCBBUY 02/19/2022 09:40
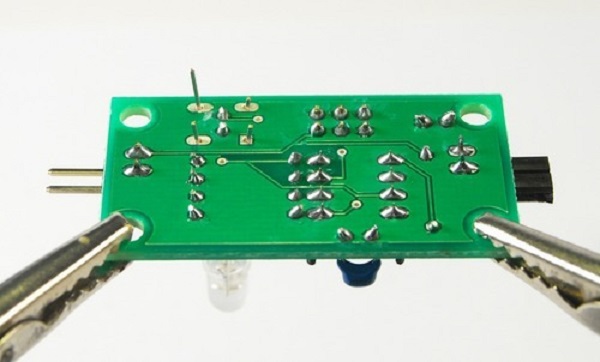
Before we get started, let us understand a little more about soldering and what it actually is. Well, soldering is essentially the process where you establish a connection between electronic components, allowing for electric current to flow for one conductor to the other.
Soldering works by heating metal wires with a soldering iron and then applying the solder to the joint. The solder acts as a glue, whereupon melting, it flows over the metals to be joined and then establishing a connection between the metals. If you are going to learn more information about solder wire on PCB, please check and read the content below in this passage.

How to prepare solder broken wire on PCB?
Before we get to the main point, eventually, we would like to suggest useful tips. The re-soldering of wires on the circuit board is similar to what we know about how to solder the electrical wire to the circuit board.
So, you shouldn’t face many issues with the re-soldering process. However, if you have forgotten the soldering process, we will recap the process for re-soldering the damaged or cracked circuit board wires.
Things you will need:
Solder: This is pretty straightforward. You will need a solder for the re-soldering process. These are available in various thicknesses that usually start from 0.02mm. The thick solders are widely used for copper pipe or PCB. It is used with a butane torch. However, you will have to opt for the thin solders for detailing and repairing jobs.
Soldering iron: You will need a quality soldering iron to generate the right amount of soldering temperature. You can opt from the low wattage (15-40W) or high wattage (60-140W) for the soldering process. The low wattage works on circuit boards, and high wattage helps work with braided speaker wire.
How to process solder broken wire on PCB?
Cut the exposed wire to length.
Clean your soldering iron tip. Pre-tin your solder iron tip. On the underside of the board, place the soldering iron so that it touches the metal around the hole and the wire at the same time. Then touch the soldering iron to the pad and wire from the opposite side.
The solder should flow around the pad and wire very quickly. Withdraw the soldering iron. Do not use the soldering iron to melt solder directly and then try to apply it to the pad and wire: solder flows towards heat, and it would rather stay on the soldering iron than transfer to the cooler pad and wire.
Also, it’s not a good idea to clip the wire after soldering as a) you may shock the solder joint so it may fail later, and b) you will be leaving copper exposed on the cut end of the wire.
Clean your soldering iron. Pre-tin your soldering iron. You are now ready for the next wire.
If you don’t feel like cleaning or pre-tinning your iron, this means your solder joint will vary over time If you do this every time, they will all be the same. When you get into a rhythm, it can take you a second or so to accomplish each solder joint.
Always, ALWAYS use the biggest soldering iron tip you can fit into the area to be soldered, rather than increasing temperature. As long as the soldering iron actually melts the solder, it’s the right temperature. By using a big soldering iron tip, you get the heat energy in there quick enough that the temperature in the board doesn’t rise too high, which can cause trace and pad delamination. A big mistake many people make is to assume that delicate electronics needs teeny-tiny soldering iron tips.
Nope. Use the biggest honking tip that will fit. Unless you have really close pad spacing or close-together connections, you really don’t want to use those tiny little tips. They are a total pain.

What are the different types of wires soldered on PCB?
A wire is an electrical piece that consists of 2 or more metal strands coated with a winding of some non-metallic origin. Such a wire serves for transporting the energy from a power source to gadgets and devices.
Any electric wire consists of 2 parts. The first one is the current-conducting part. The second part is the isolation that protects the core from external factors. As a core, copper and aluminum metals are used for wires. The insulation is made of paper, rubber, and varnish.
There is a certain classification of wires:
· Wires for winding
· Copper wires
· High resistance wires
· Mounting connectors
· Insulated for overhead lines
· Uninsulated
· Heat resistant wires
· Wires for cars
· Wires for aviation
· Wires for installation
Industry Category











