How to Understand Circuit Simulation in the PCB Industry?
By: PCBBUY 02/27/2025 17:06
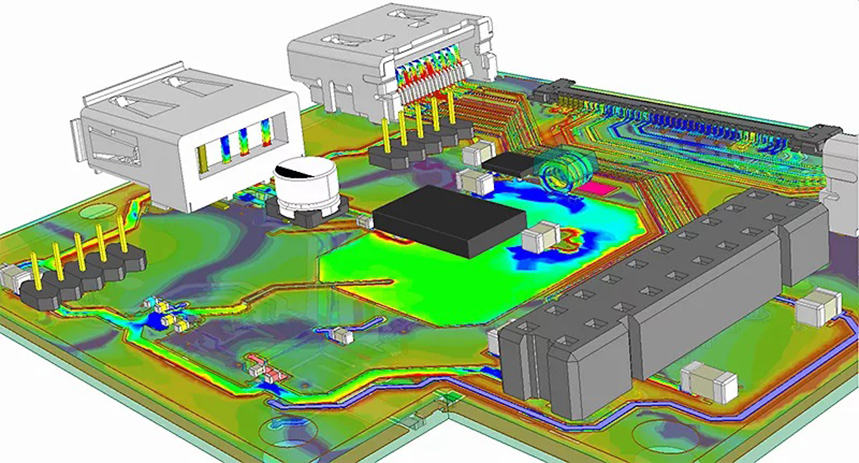
Introduction
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) industry is a cornerstone of modern electronics, enabling the development of everything from consumer gadgets to advanced aerospace systems. As PCBs become more complex, the need for accurate and efficient design tools has never been greater. Circuit simulation is one such tool that plays a pivotal role in ensuring the functionality, reliability, and performance of PCBs. This article provides a comprehensive overview of circuit simulation in the PCB industry, covering its principles, methodologies, benefits, and challenges. We will also present detailed data, comparative tables, and real-world applications to illustrate the impact of circuit simulation on PCB design and manufacturing.
Principles of Circuit Simulation
What is Circuit Simulation?
Circuit simulation is a computational technique used to model and analyze the behavior of electronic circuits before they are physically manufactured. It allows engineers to predict how a circuit will perform under various conditions, such as changes in voltage, current, temperature, or frequency. By simulating circuits, designers can identify and resolve potential issues early in the design process, saving time and resources.
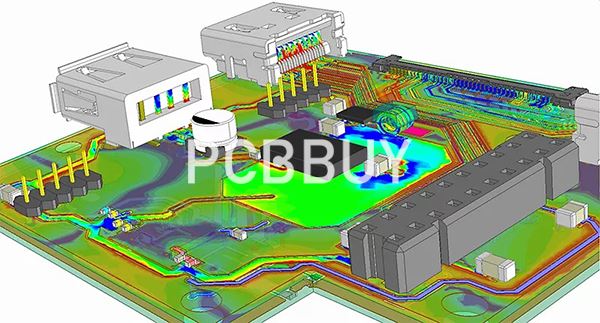
Key Objectives of Circuit Simulation
1. Performance Prediction: Simulate the electrical behavior of circuits to ensure they meet design specifications.
2. Fault Detection: Identify potential issues such as signal integrity problems, power delivery inefficiencies, or thermal hotspots.
3. Optimization: Fine-tune circuit parameters to achieve optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability.
4. Cost Reduction: Minimize the need for physical prototypes and iterative testing.
Types of Circuit Simulation
1. Analog Simulation: Focuses on continuous signals and is used to analyze components like resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers.
2. Digital Simulation: Deals with discrete signals and is used to model logic gates, microprocessors, and other digital components.
3. Mixed-Signal Simulation: Combines analog and digital simulations to analyze circuits that include both types of components.
4. Signal Integrity Simulation: Evaluates the quality of electrical signals, particularly in high-speed designs, to prevent issues like crosstalk and reflections.
5. Thermal Simulation: Predicts heat distribution and identifies potential thermal issues in the PCB.
How Circuit Simulation Works
Mathematical Modeling
Circuit simulation relies on mathematical models to represent the behavior of electronic components. These models are based on fundamental principles such as Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Laws, and Maxwell's Equations. For example, Ohm's Law is represented as:
V = I x R
Where:
V is voltage,
I is current,
R is resistance.
Simulation Algorithms
1. SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis): The most widely used algorithm for analog and mixed-signal simulation. SPICE solves systems of nonlinear differential equations to predict circuit behavior.
2. Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Used for thermal and electromagnetic simulations to analyze heat distribution and signal integrity.
3. Time-Domain Analysis: Simulates circuit behavior over time, useful for transient analysis.
4. Frequency-Domain Analysis: Evaluates circuit performance across different frequencies, essential for RF and high-speed designs.
Simulation Tools
Popular circuit simulation tools include:
LTspice: A free SPICE-based tool widely used for analog circuit simulation.
PSpice: A commercial tool with advanced features for mixed-signal simulation.
ANSYS Electronics Desktop: A high-end tool for signal integrity and thermal simulation.
Cadence Allegro: A comprehensive PCB design and simulation platform.
Benefits of Circuit Simulation in the PCB Industry
Improved Design Accuracy
Circuit simulation allows designers to verify the functionality of their designs before manufacturing, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance with specifications.
Faster Time-to-Market
By identifying and resolving issues early in the design process, simulation reduces the need for costly and time-consuming physical prototypes.
Cost Savings
Simulation minimizes material waste and rework, leading to significant cost savings in the PCB manufacturing process.
Enhanced Performance
Simulation enables designers to optimize circuit parameters for performance, efficiency, and reliability, resulting in higher-quality products.
Risk Mitigation
By predicting potential failures and performance bottlenecks, simulation helps mitigate risks associated with PCB design and manufacturing.
Challenges in Circuit Simulation
Computational Complexity
Simulating large, complex circuits can be computationally intensive, requiring powerful hardware and efficient algorithms.
Model Accuracy
The accuracy of simulation results depends on the quality of the component models used. Inaccurate models can lead to misleading results.
Integration with PCB Design Tools
Seamless integration between simulation tools and PCB design software is essential for efficient workflows. Incompatibility can lead to delays and errors.
High-Frequency and Thermal Effects
Simulating high-frequency circuits and thermal behavior requires specialized tools and expertise, adding complexity to the design process.
Data and Comparative Analysis
Performance Metrics
To evaluate the impact of circuit simulation on PCB design, several metrics are considered, including design accuracy, time-to-market, cost savings, and performance optimization. The following table compares these metrics for designs with and without simulation:
|
Metric |
With Simulation |
Without Simulation |
|
Design Accuracy (%) |
95 |
75 |
|
Time-to-Market (weeks) |
8 |
12 |
|
Cost Savings (%) |
20 |
0 |
|
Performance Improvement (%) |
15 |
5 |
Cost Comparison
The cost comparison between using circuit simulation and not using it is presented in the table below:
|
Production Volume |
With Simulation Cost (USD) |
Without Simulation Cost (USD) |
|
1-10 units |
5000 |
7000 |
|
11-100 units |
20000 |
30000 |
|
101-1000 units |
100000 |
150000 |
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of using circuit simulation versus not using it is assessed based on material waste and energy consumption:
|
Aspect |
With Simulation |
Without Simulation |
|
Material Waste (%) |
10 |
20 |
|
Energy Consumption (kWh/kg) |
15 |
25 |
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics industry, circuit simulation is used to optimize the performance of smartphones, laptops, and wearables. A case study involving a leading smartphone manufacturer demonstrated that simulation reduced design errors by 30% and improved battery life by 15%.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, circuit simulation is critical for ensuring the reliability of electronic control units (ECUs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). A case study involving an ECU manufacturer showed that simulation improved thermal management, reducing failure rates by 20%.
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense industry, circuit simulation is used to design high-reliability systems for avionics and communication equipment. A case study involving a military communication system demonstrated that simulation enhanced signal integrity, reducing maintenance costs by 25%.
Future Prospects and Challenges
Advancements in Simulation Algorithms
Ongoing research is focused on developing more efficient and accurate simulation algorithms, particularly for high-frequency and mixed-signal circuits.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning with circuit simulation tools holds great potential for automating design optimization and fault detection.
Addressing Computational Challenges
As circuits become more complex, addressing the computational challenges of simulation will require advancements in hardware and software.
Industry-Wide Standardization
Standardizing simulation models and workflows across the industry will improve compatibility and efficiency.

Conclusion
Circuit simulation is an indispensable tool in the PCB industry, enabling designers to create high-performance, reliable, and cost-effective products. By leveraging advanced simulation tools and techniques, manufacturers can overcome the challenges of modern PCB design and stay ahead in a competitive market. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of new technologies and methodologies promises to further enhance the capabilities and impact of circuit simulation, paving the way for the next generation of electronic devices.
Industry Category











