How to calculate PCB cost?
By:PCBBUY 05/28/2021 17:47
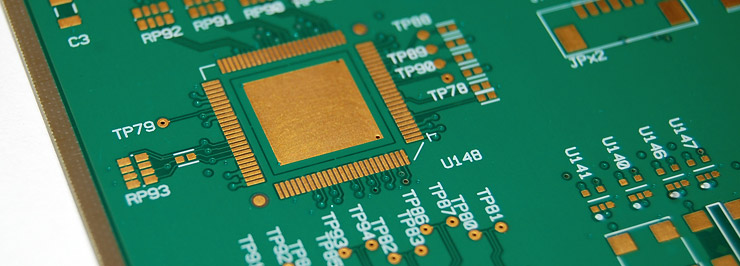
To avoid exceptionally high costs that might stem from unique PCB product design requests, calculate the potential price of your design in before production. Determine the custom specifications of the design and the steps required to bring it to fruition. Make sure these details are understood by the PCB maker to avoid costly trial and error.
In this passage we will lead you to the methods of calculating PCB cost, please read the content below to get into the topic we prepare.

What Factors Affect PCB Cost?
To calculate the cost of PCB, it is necessary to know the manufacturing process and estimate the factors that affect PCB cost.
1. Material Choice
The materials used in a circuit board will invariably affect its cost.
The factors that can impact material selection include:
Thermal Reliability: Will the board be capable of performing under the range of temperatures expected for the tasks in question? Certain boards require materials of a higher thermal rating than standard boards.
Temperature Reliability: Can the material withstand an expected range of atmospheric conditions within a controlled setting without overheating? PCBs intended for high-temperature working operations require materials that pass these tests.
Heat Transfer: Will the board withstand high-intensity loads without transferring undue levels of heat to attached and adjacent components? The right material will need to pass this test for the uses in question.
Signal Performance: Will the material facilitate uninterrupted electrical signals throughout each operating cycle of a given machine? Will the signal withstand a necessary range of temperatures and other environmental factors? These concerns are integral to the performance of a PCB.
Mechanical Properties: Does the material have sufficient physical composition to withstand a plausible range of physical stresses? Can the board be pressed into a tight slot without cracking?
2. PCB Size
The size of a PCB and its panel utilization are two of the most crucial factors that affect the price. The size of a board will generally be determined by the number of circuits required for the corresponding device.

A PCB in something as small as a digital watch will require fewer components and ultimately be less costly to produce than a computer or laptop PCB. Likewise, the PCB in a large piece of industrial machinery will be larger than the boards contained in most home electronics.
The amount of space consumed by components on a board will also affect the price. Granted, some boards are designed with less consideration of efficiency and production costs.
3. Number of Layers
Another determining factor of board price is the number of layers involved. For obvious reasons, PCBs with three or more layers cost more to produce than boards that consist of merely two layers. The pricing issue is affected by the types of material used and the size of the board itself.
Some of the most significant increases in PCB manufacturing cost occur once a second layer is added to a board. From there, an additional two boards will raise the cost by at least one-third of the previous price. The price increases are generally less steep once a design crosses the eight-layer threshold.
With each layer added to a PCB, more production steps are involved in the lamination process. This requires more time to achieve and necessitates a larger supply of material. The steps involved in multi-layer board construction also increase the possibility of production defects.
Depending on the material used in a board design, you might need more layers to ensure a solid composition. If a PCB is expected to endure a high amount of stress and still have a certain degree of flexibility, these factors will largely determine the layer count, as well as the material.
4. Finish (ENIG, HASL, etc.)
A minor factor to consider regarding PCB production involves the costs associated with a given finish. Some finishes boast higher grades and offer longer shelf life, thus adding to the overall cost of production.

Each of the surface treatment options offers unique features:
HASL: Solderability
LFHASL: Solderability
OSP: Solderability
IMM Ag: Solderability, Al wire bondable
IMM Sn: Solderability
ENIG: Solderability, Al wire bondable, contact surface
ENEPIG: Solderability, Al wire bondable, contact surface
Elec Au: Solderability, Al/Au wire bondable, contact surface
The number of layers may also determine whether the finish impacts the price of PCB production to a significant degree.
5. Size of Hole
One of the important, if not crucial, factors that can influence the cost of a PCB production is the size of the holes in a board. The costs associated with holes can also be determined by the number of holes required for the board, as well as the type of material and thickness of layers being drilled.
The sizes of the holes in a board design are the most crucial price determinants in this area. If the holes are super-thin, they will require special tools to produce. For example, a hole that has the diameter of a hair strand will be more challenging to create than a hole that equals the diameter of a typical screw hole. Such holes require more work and a specialized skill set to accomplish.
Additional hole-related factors that can impact the price of a PCB production are the thickness of the material and the number of layers contained in the board design. If a board consists of 10 or more layers, hole-drilling will be a more time-consuming task due to the thickness. If the material is super-strong and hard to drill, this will also impact the price.
6. Minimum Trace and Space
For a current to transfer on a PCB without the threat of overheating and damage to the board, there must be sufficient trace width in the board design. On boards of all sizes, a simple correlation exists between the trace width and carrying capacity. A section of the former will determine the latter. Moreover, trace cross-sections correlate to the thickness of copper.
It must be noted that trace carrying capacity does not necessarily correspond to the cross-section space. In fact, the amount of current that a trace can hold, at maximum, cannot be easily calculated, regardless of the trace width or temperature rise. The carrying capacity of a current can also be impacted by pads, vias and other board elements.
To avoid these situations, board makers will enlarge the trace width, if possible. Alternately, they can add extra solder mask to the traces that might otherwise be prone to burn. These steps can add to the price of a PCB production.
7. The Thickness of the PCB and Aspect Ratio
Until recently, the thickness of a PCB had played only a minor role in the overall cost, though all that is liable to change in the coming years.
Thinner material will generally put a line of PCBs into a slightly lower cost bracket because less material is required for the production at hand. The costs of a board in regards to thickness can also be impacted by the type of material used in a given production.
The price of a thicker board could be significantly higher if it also has a larger aspect ratio. Therefore, it might not be the thickness of the board that impacts the cost as much as the measurements or the number of layers that add to the thickness.
8. Custom or Unique Specifications
PCB manufacturing costs can also be impacted by the unique design elements in a given production. If you come to a PCB maker with custom specifications, this could raise the cost of its production, even if the board itself is small and consists of only one or two layers. The real determining factor in this regard will be whether the features in question require special tools or skills to achieve. Examples of custom specifications could include:
Contoured Edges: PCBs with rounded edges could cost more to produce, especially those that require z-axes routing.
Side-Plating: Some PCB designs specify metal edges for boosted EMC strength.
Solder Mask Clearance: If extra clearance and thickness are needed of the solder mask, this will increase costs.
Industry Category











