How to remove copper from PCB board?
By:PCBBUY 07/01/2021 17:16
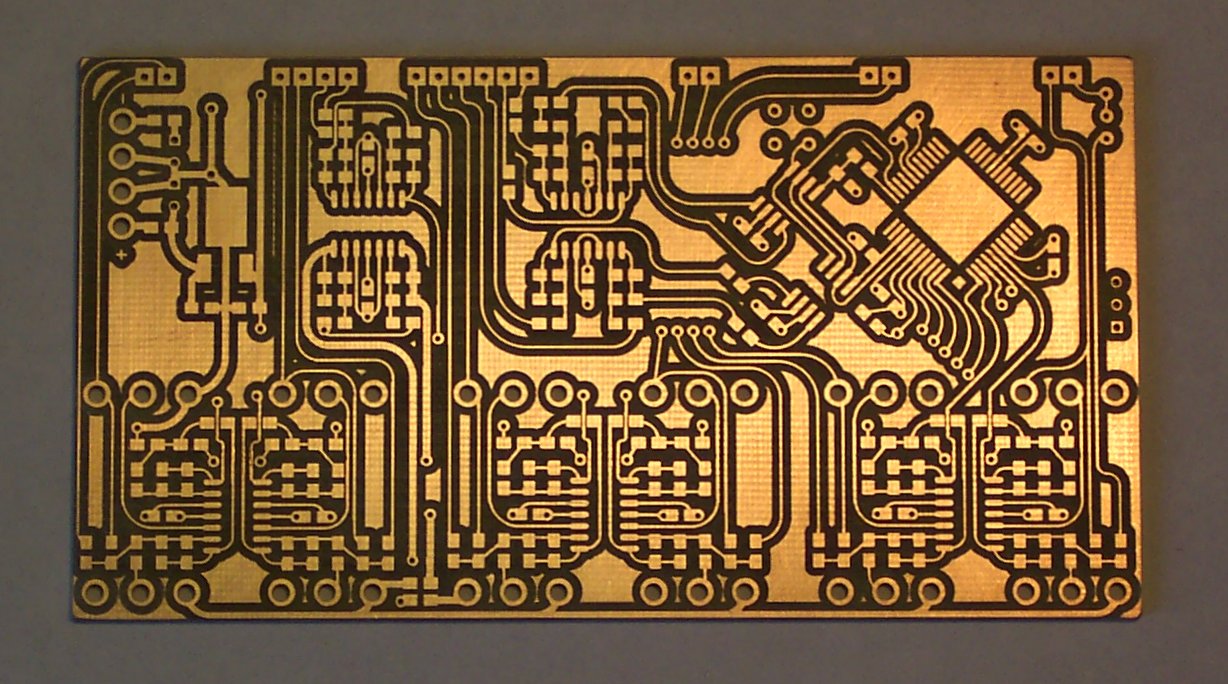
In all the PCB products, they use the different components to connect each other. And among all of them, copper plays a very important role as the most common basic conductive material. In this passage, we will focus on everything about copper PCB, please follow the content below and check for more professional information about it.

Why copper is used on PCB?
So the central question that comes to any customer's mind when purchasing copper circuit boards is why only copper is suitable. When compared to other substances, copper offers a few advantages.
Conductivity
For starters, copper offers better thermal and electric conductivity than most other metals, so heat transfers through the circuit evenly. Even heat transfer is essential in this case because otherwise, uneven heating can put excessive stress on the PCB, which damages its components.
Copper has impressive electric conductivity, which means it transmits signals with minimal electrical energy loss.
Efficient
Because of its conductive properties, printed circuit board manufacturers don't need countless tones of copper. Each copper circuit board will only require minimal amounts for proper functioning. From this angle, one ounce of copper makes for a copper layer thickness of 35 micrometers, which is enough to cover a whole square footing of a PCB substrate.
Availability
Most importantly, copper is readily available, which makes it comparatively less expensive than other metals.
Improves Electronics' Reliability
Copper has an unmatched thermal resistance. This factor can increase the reliability of electronic devices that have to operate in harsh environments, such as those with high temperatures.
Reduces Assembly Costs
Thanks to copper's even heat transfer capabilities, PCB manufacturers can install heat sinks onto the surface or build boards with one side entirely covered by a layer of copper, which also acts as a heat sink.
Regardless of the method selected by copper circuit board manufacturers, they cut the assembly process short, which significantly reduces manufacturing expenses.
How to remove copper from PCB?
One of the most exciting conversations surrounding copper circuit boards is how manufacturers, developers, and engineers can retrieve copper from old PC boards. The thin layer of copper adhering to a PCB is in the form of traces or wiring that sends an electrical current to all the soldered components and other circuits.
After removing the soldered-on electronic components, it's possible to recycle copper traces. These have to be stripped and sent to a specific recycling center.
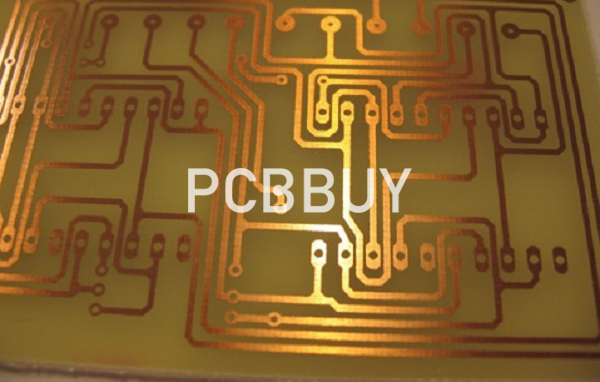
Start by using your hobby knife to cut each copper trace that begins on one end. Use pliers to grasp one of the cut ends. It may be complicated to get under a copper trace, so it's easier to start the process by prying up the evidence using the tip of your knife.
Once you grasp it, pull the copper trace away from the copper PCB board, so it comes off cleanly. This step is just for one copper trace – developers have to repeat this countless times on different trails.
How to reserve copper PCB?
Copper PCBs are prone to corrosion and oxidation, both of which can impact the efficiency of the board. Here's how to protect your PCBs from corrosion and oxidation.
Request a Finish
First and foremost, you should request your PCB manufacturer for a protective layer that covers the copper. The solder mask, in this case, helps in preventing parts of the circuit where you didn't solder from oxidation.
However, you can't use a solder mask in all circuit boards since it affects performance at high frequencies.
Keep the PCBs Away From Humidity
Upon receiving your PCBs from the manufacturer, you'll notice that they're vacuum-sealed. It is the optimal condition to keep them in since it protects them from humidity and moisture. Once you remove them from the packaging, you should invest in a humidity-free container to hold them back.
Apply a Conformal Coating
After soldering the PCB, it recommends that you protect the board with conformal coating before integrating it in the desired electronic device. These lacquers or varnishes preserve the circuit from oxidation and corrosion.
Keep Your PCBs from Coming into Contact with Corrosive Metals
Depending on the enclosure you integrate the PCB in, it can still destroy or oxidize. For instance, plastic pens are entirely closed off, effectively preventing corrosion. On the other hand, you may select a metal-based ring for harsh environments.
Metallic enclosures often include aluminum, which is a highly corrosive metal. Keeping copper PCBs in such proximity to aluminum can lead to oxidation, so treat the ring accordingly.
Rely on Hermetic Sealed Packaging
You can rely on hermetically sealed packages to prevent environmental conditions from affecting the PCB. However, closing the PCB in the container has to be completed in a controlled environment. It can keep any moisture from being trapped inside the packaging and destroying the PCB.
Industry Category











