PCB Copper to Edge Clearance Explained Simply
By:PCBBUY 12/23/2025 16:40
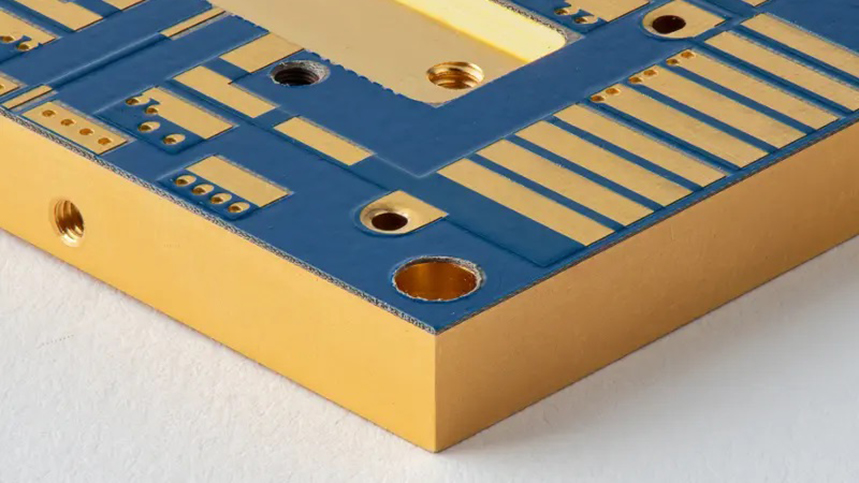
PCB copper to edge clearance means the distance between copper features and the edge of the circuit board.
If copper is placed too close to the board edge, it may be damaged during manufacturing or cause electrical problems in real-world use. In PCB manufacturing, copper to edge clearance must consider routing tolerances, depanelization methods, and IPC standard recommendations.
Why Copper to Edge Clearance Is Important?
Proper copper to edge clearance is essential for several reasons:
-
Electrical safety: Prevents short circuits, arcing, or breakdown near the board edge
-
Mechanical reliability: Avoids copper exposure or damage during routing, V-cut, or depanelization
-
Manufacturing yield: Reduces scrap caused by exposed copper or edge defects
-
Compliance with IPC standards: Ensures designs meet industry-accepted guidelines
For high-reliability or high-voltage applications, insufficient clearance can result in serious functional failures.

PCB Copper to Edge Clearance per IPC Standards
According to IPC design guidelines such as IPC-2221, copper features should maintain a minimum clearance from the board edge to account for manufacturing tolerances and electrical requirements.
While IPC provides general recommendations rather than strict mandatory values, typical considerations include:
-
Product class (consumer, industrial, high-reliability)
-
Operating voltage
-
Board thickness and copper weight
-
Edge processing method (routing, V-cut, punching)
Designs intended for harsh environments or higher voltages usually require larger copper to edge clearance than basic consumer electronics.

Factors Affecting Copper to Edge Clearance Requirements
PCB Edge Processing Method
Routing, V-cut, and scoring processes each have different tolerances, directly influencing the required clearance.
Copper Thickness and Layer Structure
Thicker copper increases the risk of edge exposure, especially on outer layers and internal copper planes near the board outline.
Application Environment
Industrial, automotive, or high-voltage PCBs typically require more conservative clearance values.
Common Problems Caused by Insufficient Copper to Edge Clearance
If copper is placed too close to the PCB edge, manufacturers and end users may face:
-
Exposed copper after routing or depanelization
-
Electrical short circuits or edge breakdown
-
Reduced mechanical strength at the board edge
-
Failure during reliability or safety testing
These issues often lead to rework, delays, or increased production cost.
PCBBUY’s Capability in Controlling Copper to Edge Clearance
PCBBUY applies strict control over pcb copper to edge clearance through:
-
Detailed DFM review of Gerber files before production
-
Controlled board outline machining and depanelization processes
-
Clear communication with customers when clearance risks are detected
-
Experience handling multilayer, HDI, and high-reliability PCB designs
By combining IPC knowledge with manufacturing expertise, PCBBUY helps customers avoid clearance-related failures.
Design Recommendations for IPC-Compliant Copper to Edge Clearance
To improve manufacturability and reliability, designers should:
-
Avoid placing copper features too close to the board outline
-
Allow additional clearance for routed edges and thick copper designs
-
Consult with the PCB manufacturer early if clearance is limited
PCBBUY’s engineering team can provide DFM suggestions to optimize copper to edge clearance before production.
Conclusion
PCB copper to edge clearance is a small design detail with a major impact on reliability and manufacturability.
With IPC-based guidelines and strong process control, PCBBUY ensures stable production and high-quality results for demanding PCB applications.
FAQ
What is PCB copper to edge clearance?
It is the minimum distance between any copper feature and the physical edge of the PCB.
What IPC standard covers copper to edge clearance?
IPC-2221 provides general design guidance for PCB copper to edge clearance.
Why is copper to edge clearance important?
It prevents copper exposure, electrical shorts, and mechanical damage during manufacturing and use.
What happens if copper is too close to the PCB edge?
It may be damaged during routing or depanelization, leading to exposed copper or electrical failure.
Can PCBBUY help check copper to edge clearance?
Yes. PCBBUY performs DFM reviews and can advise on copper to edge clearance based on IPC guidelines and manufacturing capability.
Industry Category











