PCB Material Properties
By:PCBBUY 09/01/2021 09:28

When you need to select a PCB substrate material, which PCB material properties are most important for your board? The answer depends on the board’s application and the environment where the PCB will be deployed.
If you are looking for the information of PCB material, please check and read the content we prepare to learn more information about it.
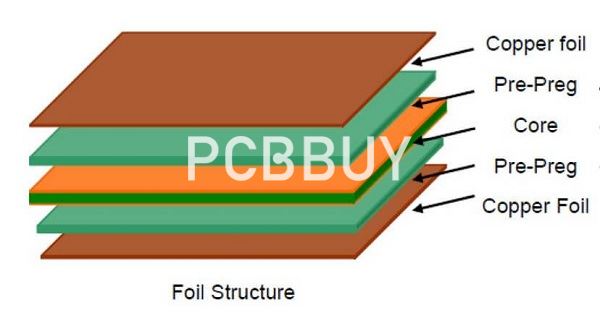
What is the importance of PCB material properties?
Your substrate selection is no longer limited to FR4, but you should not make the decision of PCB laminate selection lightly. You should first understand how different material properties affect your PCB and choose a laminate that satisfies your operational requirements accordingly. Don’t just listen to marketing speak from laminate manufacturers; take time to understand each of the substrate material properties and how they affect your PCB quote.
Some data for PCB material properties can be found online, but it’s best to consult with manufacturers, particularly for specialized laminate materials as no two laminates are exactly the same, nor are two lots exactly the same. More exotic materials such as ceramics and metal-core PCBs give a range of unique material properties.
The important PCB material properties all designers should understand fall into four areas: electrical, structural, mechanical, and thermal properties.

What are the mechanical properties of PCB material?
Peel Strength
Peel strength is a measure of the bond strength between the copper conductor and the dielectric material. It is expressed in pounds of force per linear inch (PLI, or average load per conductor width) required to separate bonded materials where the angle of separation is 180 degrees.
Peel strength tests are done on samples of copper traces of 1 OZ thick and ~ 32 to 125 millimeters wide after standard PCB manufacturing processes. It is completed under 3 conditions:
• After thermal stress: after a sample is floated on solder at 288 ºC for 10 seconds
• At elevated temperatures: after a sample is exposed to hot air or fluid at 125 ºC
• After exposure to process chemicals: after a sample is exposed to a specified series of steps in a chemical or thermal process
Flexural Strength
Flexural strength is the measure of a material’s capability to withstand mechanical stress without fracturing. It is expressed in either Kg per square meter or pounds per square inch (KPSI).
Flexural strength is generally tested by supporting a PCB at its ends and loading it in the center. IPC-4101 is the Specification for Base Materials for Rigid and Multilayer Printed Boards, and it gives the minimum flexural strength of various PCB materials.
Young’s Modulus
Young’s modulus, or tensile modulus, also measures the strength of a PCB material. It measures the stress/strain ratio in a particular direction, and some PCB laminate manufacturers give strength in terms of Young’s modulus instead of flexural strength. Like flexural strength, it is expressed in force per unit area.
Some PCB laminate manufacturers give the PCB materials strength not in terms of Flexural Strength but in terms of Young’s modulus which is a measure of Stress/strain ratio in a particular direction.

What are the chemical properties of PCB material?
Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption is the ability of a PCB material to resist water absorption when immersed in water. It is given by a percentage increase in weight of a PCB material due to water absorption under controlled conditions as per standard test methods. Most materials have moisture absorption values in the range of 0.01% to 0.20%.
Moisture absorption affects the thermal and electrical properties of the material, as well as the ability of the material to resist conductive anode filament (CAF) formation when a PCB circuit is powered.
Methylene Chloride Resistance
Methylene chloride resistance is a measure of a material’s chemical resistance; specifically, the ability of a PCB material to resist methylene chloride absorption.
Just like moisture absorption, it is expressed by a percentage increase in the weight of a PCB material due to exposure to or soaking in methylene chloride under controlled conditions. Most PCB materials have methylene chloride resistance values in the range of 0.01% to 0.20%.

What are the special materials PCB material properties?
Rather than the aforementioned materials, we also utilize several special materials to assemble high frequency circuit boards. Here are some typical materials that we use for such circuits:
Rogers Corporation: These materials are FR-4 compatible, and are engineered for your exact performance requirements. These materials provide excellent results owing to their superior mechanical properties such as low dielectric loss, low signal loss, high thermal conductivity, and controlled impedance.
Arlon: These high performance laminates with specialized electrical, thermal, mechanical, or other performance characteristic are largely used in wireless communications infrastructure, military and commercial avionics, and semiconductor test and measurement equipment.
High Tg: This refers to high glass transition temperature. We employ these materials for PCBs used in critical and demanding applications including printed circuit boards exposed to high thermal loads. The material offers excellent performance at high temperatures, and exhibits good delamination property.
Industry Category











