PCB Thermal Paste
By:PCBBUY 08/30/2021 09:16

Thermal paste is also called heat sink compound or thermal grease and conducts heat in the same manner as the thermal pad. While thermal paste is made out of similar materials as the thermal pads, it comes in a liquid form that can be manipulated to fit the area that requires the thermal interface material. Thermal paste between the heat-generating component and the heat sink will close any air gaps between the two.
Are you interested in PCB manufacturing knowledge?Welcome to check and read the content below for more about it to learn more professional information. Let’s go!
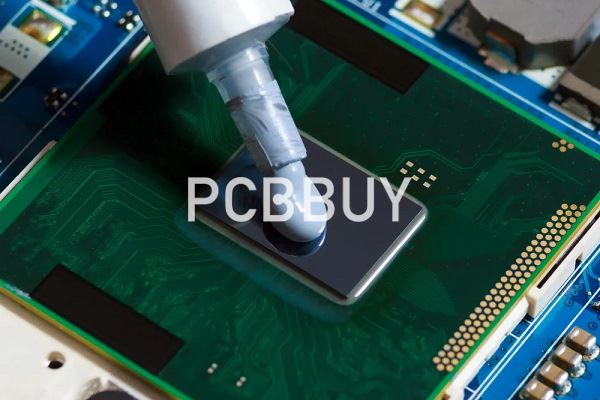

What is the basic introduction of PCB thermal paste?
The most generic definition for thermal paste is that it is a paste chemically constructed to allow for heat transfer. Its composition is a liquid polymer, that may include urethanes, acrylates, silicones and epoxies. The most typical function for thermal paste is as a filler between two surfaces to provide a solid interface and increase the volume of heat transfer between the surfaces.
With this primary function it may be surprising that the heat transfer rate may range from approximately 3W/(m·K) to 13W/(m·K) for non-metallic pastes, which is far below the 385W/(m·K) for 99% pure copper.

Why PCB thermal paste is important for manufacturing?
It is well-known that the removal of excess heat from components or parts that tend to generate high temperatures is critical during electronics operation. Heat sinks that can have thermal conductivities greater than 200W/(m·K), are common for these components, which include CPUs, GPUs, power transistors and other high-performance semiconductor-based devices.
During operation, the greatest source of heat on circuits boards is generation by components. And the heat removal techniques implemented are done so during PCB assembly. However, the assembly process itself introduces heat to the board, which also should be a design consideration. There are two heat transfer issues, dissipation and distribution.
To be most effective, thermal paste should fill in all of the gaps between the two surfaces at which it is applied. Additionally, it is desirable that the paste not conduct electricity away from the component. Another important consideration is operational lifetime. For thermal pastes, typical ranges are 3-5 years, which means that for many components it may need to be replaced. All of these factors must be considered if it is determined that thermal paste should be utilized for your design.
![]()
What are the advantages of PCB thermal paste?
· Reliable
· Inexpensive
· Easy application
· Fills gaps well
· Thin layer
Thermal paste is like an old swimming hole out in the woods. You know it’ll always be there, and it’s cheap, but things might get a bit messy. However, just like sunscreen is cheaper than skin cancer treatment, thermal paste is less expensive than PCB thermal pads.
When to use PCB thermal paste?
Thermal paste also bests thermal pads when it comes to uneven surfaces. Since thermal paste is a liquid, it can fill large gaps more evenly than thermal pads. Some heat sinks or ICs have uneven surfaces where the TIM will be applied. If that’s the case for your PCB, thermal paste will provide better thermal conductivity than a thermal pad.
Remembering which of your components need heat sinks can be a pain. Instead of straining your brain, let your PCB design software do it for you. Most design programs will let you add in comments on components. Attach thermal performance concerns to an electronic component to keep your PCB quote out of hot water.
What are the applications of PCB thermal paste?
Carriers and fillers
The carrier material in a thermal paste is typically categorized as silicone or non-silicone type. Generally, manufacturers recommend using silicone-based pastes.
Heatsink specification
The surface finish of the heatsink is also a critical part of the thermal interface. Specifications for roughness, unevenness over distance, are to be considered along with the use of a baseplate for the component or module.
Applying to component VS applying to heatsink
The order of assembly during the production process will decide if you need to apply the paste to the component first or the heatsink.
Preparation of paste
Pastes will have to be mixed before application to check for homogenization of the carrier and filler materials.
Industry Category











