What Are the Applications of Ceramic PCB in Manufacturing?
By:PCBBUY 05/08/2023 15:17
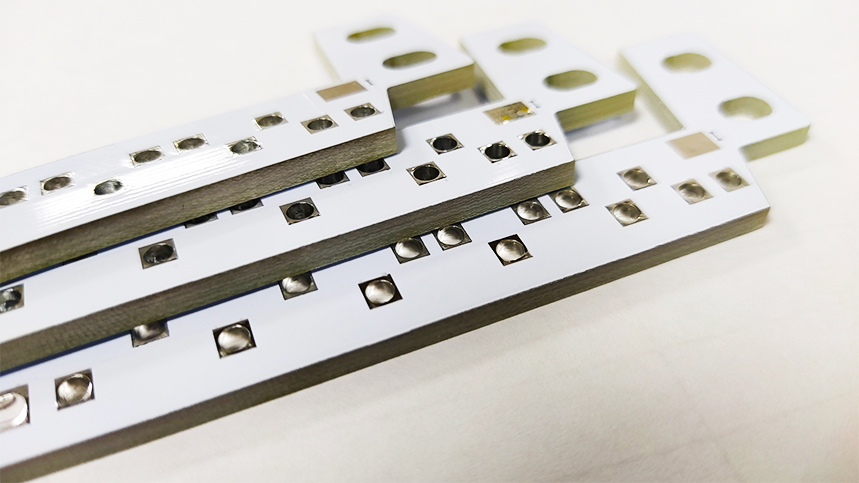
With the continuous development of electronic devices towards multi-functionality, miniaturization, and high-speed operation, as well as the increasing scale of integrated circuits (ICs), ceramic printed circuit boards (PCBs) are facing more stringent requirements in terms of coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), thermal conductivity, dielectric loss, dielectric constant, and tape resistance. It is foreseeable that ceramic PCBs using aluminum nitride, mullite, and glass-ceramic as substrate materials will witness a growing demand in the future.
If you are looking for more information of ceramic PCB, please check and read the content below for more professional knowledge.

What are the applications of ceramic PCB?
Ceramic PCBs are used in various high - tech fields. Here are some of their main applications in simple terms:
Why is ceramic PCB so popular?
High Thermal Expansion
The first reason why ceramic boards are so popular in the electronics sector is their excellent thermal coefficient expansion. It is good to note that the ceramic base heat transmission almost matches silicon and can act as a connection material. Besides, you can use it as an isolator. Therefore, there is maximum use for the thermal properties of ceramic boards, even in adverse conditions.
Stability
The application of ceramic brings a stable dielectric capacity, and you can modify the balance into a partial radiofrequency loss to increase your device's power. Still, despite the surface toughness, ceramic materials come with an inherent resistance against chemical erosion. Ceramic's chemical resistance can change to resistance against liquids and moisture.
Versatility
You can create several use cases to integrate a metal core board with a high thermal expansion. Besides, you can still turn the metal core into reliable conductors using the sintering technique. Therefore, the application of ceramic PCB is beneficial because of its high processing temperatures.
Durability
The ceramic board fabrication process creates durability through the use of unique properties, such as toughness. That prevents your PCB from wear and tear. So you can be confident that you will not change your PCB soon because of its slow aging capacity. Also, the high thermal resistance of ceramic PCB makes it assume a decelerated decomposition process.
Adaptability
Lastly, the use of metal cores can serve as inflexible carriers that offer mechanical stiffness. This property makes it easier to use ceramic PCBs in any state of matter because of the high resistance to corrosion and normal wear and tear.
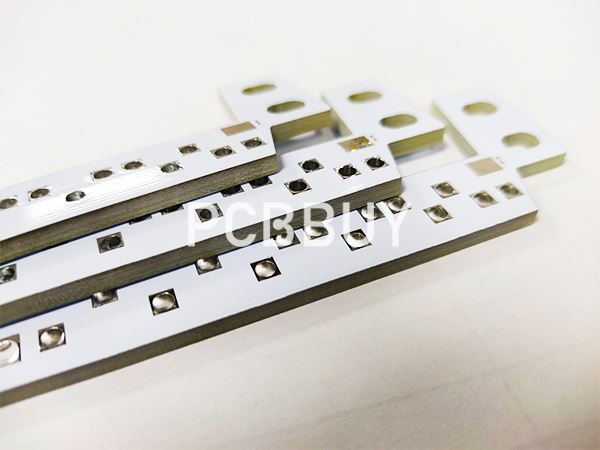
What are the main types of ceramic PCB?
The ceramic PCBs are classified into three types based on the manufacturing process.
· High Temperature Ceramic PCB
· Low Temperature Ceramic PCB
· Thick Film Ceramic PCB
High Temperature Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards
This type of PCB is designed for high temperatures and is sometimes referred to as a high temperature co-fired ceramic (HTCC) circuit. These circuit boards are manufactured in a unique manner. To create new ceramics the process combines solvent, plasticizer, adhesive, aluminum oxide, and lubricant.
Once the new ceramic has been developed, it is coated, and circuit tracing on molybdenum or tungsten metals is applied. Following this, the circuits will be baked between 1600 and 1700 degrees Celsius for approximately 48 hours after lamination. The baking will take place in a specific gaseous environment that will include hydrogen gas.

Low Temperature Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards
This type of PCB is designed for low temperatures and is sometimes referred to as a low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTTC) circuit. The low-temperature ceramic PCB manufacturing process differs from the high-temperature or HTCC type. The adhesive substance and crystal glass are used to make the low-temperature ceramic PCB. Both of these materials are applied to a metal sheet with gold paste. Following this, the board will be cut and laminated. Finally, the circuit will be kept at 900 degrees Celsius in a gaseous oven.
The low-temperature ceramic PCB has better shrink tolerance and less warpage. In summary, LTTC will have higher thermal conductivity and mechanical intensity than other types, including HTCCs. The thermal advantage of the low-temperature PCB makes it preferable when working with heat-free products such as LED lights.
Industry Category











