What Are the Features of Turnkey PCB Assembly?
By:PCBBUY 09/27/2024 16:21
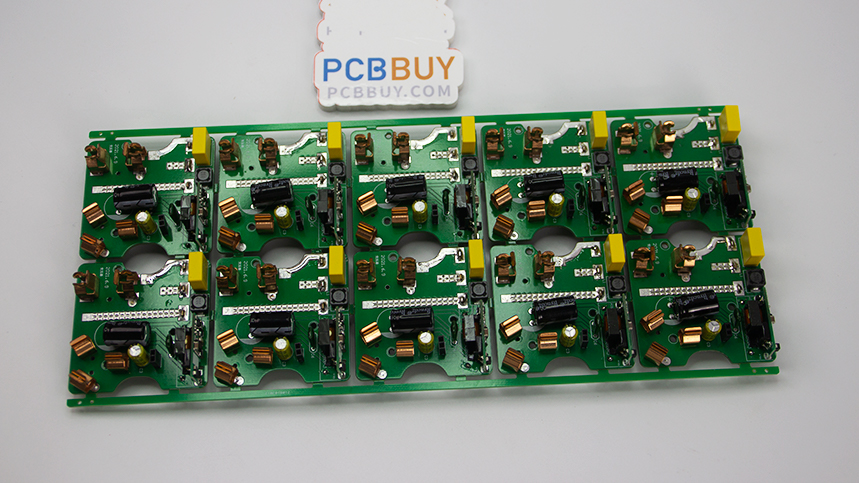

Turnkey PCB assembly is a comprehensive service that provides a complete solution for the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs), from design and manufacturing to assembly and testing. This article explores the features of turnkey PCB assembly, including its benefits, processes, and technologies involved, supported by relevant data and comparisons.
1. Understanding Turnkey PCB Assembly
1.1 Definition of Turnkey PCB Assembly
Turnkey PCB assembly refers to a service model where a single provider manages all aspects of PCB production, allowing customers to receive fully assembled and tested boards ready for installation. This approach minimizes the need for multiple vendors and streamlines the production process.

1.2 Components of Turnkey PCB Assembly
Key components of turnkey PCB assembly include:
Design Services: Assistance in designing the PCB layout using CAD software.
Procurement of Components: Sourcing all necessary electronic components.
Fabrication: Manufacturing the PCB based on the design specifications.
Assembly: Placing and soldering components onto the PCB.
Testing: Conducting functional and reliability tests to ensure quality.
2. Advantages of Turnkey PCB Assembly
2.1 Cost Efficiency
Turnkey PCB assembly can significantly reduce costs associated with:
Vendor Management: Minimizing the number of suppliers reduces administrative overhead.
Bulk Purchasing: Turnkey providers often benefit from economies of scale when purchasing components.
2.2 Time Savings
By consolidating processes, turnkey assembly accelerates time-to-market. Key factors include:
Streamlined Communication: Direct communication with a single provider enhances coordination.
Reduced Lead Times: Efficient processes can lead to faster production cycles.
2.3 Quality Assurance
Turnkey providers implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the assembly process. These may include:
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Ensuring proper component placement and solder quality.
Functional Testing: Verifying that the assembled PCB meets performance specifications.
3. The Turnkey PCB Assembly Process
3.1 Design and Prototyping
The first step in turnkey PCB assembly is the design phase, which involves:
Schematic Capture: Creating a visual representation of the electronic circuit.
Layout Design: Converting the schematic into a PCB layout, considering factors such as trace width and spacing.
3.2 Component Sourcing
Once the design is finalized, the turnkey provider sources all required components, considering:
Component Availability: Ensuring that all components can be obtained within the required timeline.
Quality of Components: Selecting reputable manufacturers to guarantee reliability.
3.3 PCB Fabrication
The fabrication process includes several steps:
3.3.1 Material Selection
Choosing the right materials is essential for performance. Common substrate materials include:
FR-4: A fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin, widely used for standard PCBs.
Polyimide: For high-temperature applications.

3.3.2 Manufacturing Steps
The manufacturing process typically involves:
1. Photoengraving: Transferring the PCB design onto a copper-clad laminate using photolithography.
2. Etching: Removing excess copper to create the desired circuit patterns using solutions such as ferric chloride (FeCl3):
Cu + FeCl3 →CuCl2 + FeCl2
3. Drilling: Creating holes for component leads.
3.4 Assembly
In the assembly phase, components are placed on the PCB. Key methods include:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Involves soldering components directly onto the surface of the PCB.
Through-Hole Technology: Components are inserted into holes and soldered on the opposite side.
3.5 Testing and Quality Control
After assembly, comprehensive testing ensures the functionality and reliability of the PCB. Methods include:
In-Circuit Testing (ICT): Identifying defects in the circuit.
Thermal Cycling Tests: Assessing the durability of solder joints under temperature variations.
4. Technologies Involved in Turnkey PCB Assembly
4.1 Automated Assembly Equipment
Automated systems play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Key technologies include:
Pick-and-Place Machines: Automating component placement with high precision.
Reflow Ovens: Used for soldering SMT components, providing controlled heating profiles.

4.2 Advanced Testing Technologies
Turnkey providers utilize advanced testing technologies, such as:
X-Ray Inspection: Non-destructive testing to check for hidden solder joints.
Functional Testing Software: Simulating real-world conditions to verify performance.
Table 1: Comparison of Testing Methods
|
Testing Method |
Description |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|
In-Circuit Testing |
Tests each component individually |
High fault detection rate |
Requires specific test fixtures |
|
Functional Testing |
Tests overall functionality |
Validates product performance |
May miss certain faults |
|
X-Ray Inspection |
Inspects solder joints |
Non-destructive |
Limited to certain defects |
5. Challenges in Turnkey PCB Assembly
5.1 Component Obsolescence
As technology evolves, components may become obsolete, leading to sourcing challenges. Turnkey providers must continuously adapt to changing component availability.
5.2 Quality Control
Maintaining consistent quality across all processes can be challenging, especially with high-volume production. Implementing robust quality assurance protocols is essential.
5.3 Complexity of Designs
As electronic devices become more complex, the design and assembly process must adapt. This complexity requires advanced manufacturing techniques and thorough testing to ensure reliability.
Conclusion
Turnkey PCB assembly offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, time efficiency, and improved quality assurance. By consolidating all aspects of PCB production, manufacturers can streamline their operations and enhance product reliability. As technology continues to advance, the turnkey assembly model will play an increasingly vital role in the electronics industry.
References
1. Friedman, A. (2020). "The Future of PCB Assembly: Trends and Challenges." Journal of Electronic Materials.
2. Hwang, J. (2021). "Understanding Turnkey PCB Services: A Comprehensive Guide." International Journal of Electronics.
3. Katz, R. (2022). "Advancements in PCB Manufacturing Technology." Journal of Materials Science.
4. Liu, Y. & Zhang, T. (2023). "Quality Assurance in PCB Assembly: Methods and Practices." IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology.
5. Sullivan, J. (2024). "Testing Methods for PCB Assembly: A Review." Soldering & Surface Mount Technology.
Industry Category











