What Are the Main Types of PCB Assembly Soldering Material?
By:PCBBUY 04/25/2024 14:21
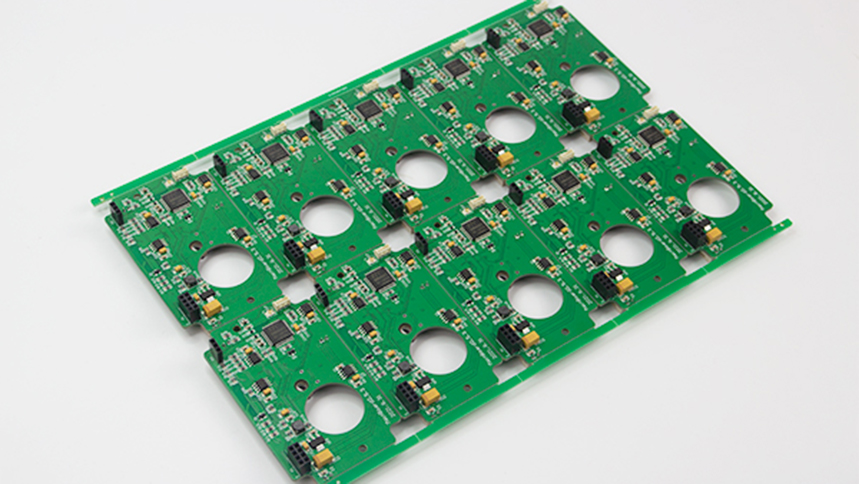
The printed circuit board can only be functionalized after the electronic components are assembled on its surface to achieve the correct connection. Failure analysis shows that the failure problem of the printed circuit board is mostly attributed to the assembly process of the electronic components. Therefore, the assembly technology of printed circuit board electronic components plays an important role.
The assembly technology of printed circuit board includes the selection of assembly materials, assembly process design, and assembly technology and assembly equipment. Any link has a serious impact on the final reliability of the printed circuit board. With the increasing density of PCB board interconnect, the size of pad and the distance between pad are getting smaller and smaller, which brings great challenges to PCB assembly technology. Although many new connection technologies have appeared in printed circuit board assembly in recent years, the assembly of electronic components through high temperature connection of solder still occupies a dominant position.

This article will systematically introduce the welding materials and welding technology of wave soldering and reflow welding, which are the most commonly used processes in the assembly of printed circuit boards.
What is the Basic of Assembly Solder?
Solder is a key "bridge" material for interconnection assembly between printed circuit boards and electronic components. In order to ensure good reliability during the welding process, the solder is usually a fusible metal. Solder has been greatly developed with the progress of technology, especially in the field of brazing micro-components, and has become an indispensable assembly material.
After welding, the solder can not only form an alloy on the metal surface of the pad, but also weld the connection points together, and the melting point is lower than that of the fund, and it is easy to form an alloy with the fund. The PCB soldering process requires both adequate mechanical connections and good electrical connections.
In general, solders with a melting point below 450C are called "soft solders". This kind of solder is mainly composed of tin. In order to meet the requirements of various brazing, different alloy components are added to it, such as lead, copper, silver, gold, zinc, pot, magnesium aluminum, steel, secret, boron, silicon, germanium and other elements to improve or reduce its melting point. Among them, tin-lead solder is the most common type of welding material in printed circuit board product assembly technology. Despite the impact of lead-free technology on the application of tin-lead solder, tin-lead solder is still used in the military field on a large scale.

What is the Basic of Tin and Lead Solder?
Printed circuit board pad surface metals such as nickel, copper, silver, gold, platinum and their alloys can form alloys with tin, so as to obtain good mechanical and electrical connections. Therefore, tin is an indispensable metal material in the assembly technology of printed circuit boards. However, due to some shortcomings in physical properties of pure tin, pure tin cannot be directly used as solder for printed circuit board assembly. A certain amount of lead is added to tin metal to form tin-lead alloy, which can obtain excellent properties of both tin and lead. Tin-lead alloy has the following excellent properties:
1. Lower melting point
The melting point of tin and lead is 232C and 327C respectively. After adding a certain amount of lead to tin, a low melting point alloy with point 183 can be obtained, which is conducive to welding.
2. Improve mechanical properties
The tensile strength of tin is 14.7N/mm, and that of lead is 13.7N/mm. When these two metals are mixed to form alloys, their tensile strength can reach 39.2~49N/mm. The shear strength of tin is 19.6N/mm2, the shear strength of lead is 13.72N/mm, and the shear strength of the alloy formed by these two metals is 29.4 ~34.3N/mm, and this number will increase after the coal connection. Table 10-1 lists the physical and mechanical properties of solder series.
|
Temperature/℃ |
Tin60-Lead40 |
Tin40-Lead60 |
||
|
Tensile strength(N/mm2) |
Elongation(%) |
Tensile strength(N/mm2) |
Elongation(%) |
|
|
20 |
56.41 |
60 |
34.63 |
539 |
|
50 |
46.60 |
80 |
43.26 |
705.6 |
|
75 |
41.69 |
90 |
38.65 |
784 |
|
100 |
30.90 |
110 |
24.72 |
960.4 |
|
125 |
19.33 |
180 |
15.50 |
1960 |
|
150 |
12.36 |
180 |
11.58 |
1960 |
|
200 |
Melt |
Melt |
Melt |
Melt |
3. Reduce surface energy
Due to the presence of lead, the expansion area of the alloy can be doubled, thus reducing the surface energy of the alloy
4. Can enhance
The antioxidant capacity of the solder, reduce the amount of oxidation of small amounts of other metal impurities have a great impact on the performance of tin-lead solder, some play a positive role, some are bad. According to the functional properties of these metals, some metals can be consciously incorporated to improve certain characteristics of the solder, and try to eliminate harmful impurities. For example:
1) Zinc (Zn): When the content is about 0.001% (mass fraction), it has an adverse effect on the appearance of the solder joint, the fluidity and wettability of the solder, and is one of the most taboo impurities in welding.
2) Aluminum (AI): When the content reaches 0.001% (mass fraction), it is harmful to the fluidity and wettability of the solder, not only affecting the appearance of the solder joint, but also prone to oxidation and corrosion.
3) (Cd): It has the effect of increasing the solder at the melting point, and makes the solder grain become coarse and tarnish when the content exceeds 0.001% (mass fraction), the fluidity of the solder decreases and the solder becomes brittle.

4) Brocade (Sb): can increase the mechanical strength and resistivity of solder at the melting point, when the content is 0.3% ~3 (mass fraction)%, the solder joint formation is excellent; Within 6% (mass fraction), it can not only increase the strength and creep resistance of the solder joint, but also have no adverse effects; However, after the content exceeds 6% (mass fraction), the solder becomes hard and brittle, and the fluidity and wettability become worse, and the corrosion resistance is also worse, and the solder containing gold is not suitable for the welding of zinc base metals
5) (Bi); Reduce the melting point of the solder and make it brittle.
When it contains a small amount, although the fluidity of the solder can be slightly increased, it affects the appearance and makes the solder
6) Arsenic (As):
The hardness and brittleness increase.
7) Iron (Fe): make the solder magnetic, and increase the melting point, not easy to operate
8) Copper (Cu): increase the melting point, increase the bonding strength, increase the creep resistance when the content is 1% (mass fraction), can inhibit the corrosion of the solder on the electric soldering iron head, and can weld fine lines.
9) Phosphorus (P): When the content is small, the fluidity of the solder can be increased, but when the content is too high, the ability of the molten iron head in the printed circuit board assembly process, the purity of the tin-lead solder needs to be strictly controlled to avoid the introduction of the solder performance. Deterioration of harmful metals.
In addition, during the welding process, the copper foil of the printed circuit board, the copper of the component lead wire and its coating metal will continue to dissolve into the solder tank, causing pollution to the solder. With the progress of welding process, the impurities continue to accumulate, and the content gradually increases. If the standard is exceeded, welding quality problems will occur, resulting in failure problems. Therefore, in the printed circuit board manufacturing assembly process to often check and control the solder composition, serious, must replace all the solder to maintain normal production and ensure product quality.
What is the Basic of Tin-lead Multi-alloy Solder?
In order to obtain some useful characteristics of tin-lead solders, metal components such as silver, secret and so on are often added to construct multi-alloy solders.
1. Silver blending
Adding a small amount of silver into the tin-lead alloy can not only reduce the melting point of the solder, but also make its diffusion better and the solder joint beautiful and bright. From the economic point of view, taking into account the operation and melting point and other factors, the general silver content of 0.5% to 2% (mass fraction). This kind of solder is mainly suitable for crystal oscillator, ceramic parts, thermistors, thick film components, integrated circuits and silver plated parts, and can also be used as high temperature soft solder.
Adding silver to the solder beforehand can inhibit the diffusion of silver coated on ceramic and mica sheets to prevent spalling of the silver layer, which is a characteristic of silver-containing solders. In the dip welding of printed circuits, especially phenolic resin printed circuit boards, special attention should be paid to the migration of silver when using silver containing solder.
The silver content should be strictly controlled. If silver is mixed too much (mass fraction above 3%), the solder will lose luster and the spot welded will be granular, and the practicality will be affected
2. Blending
Mixing secret can reduce the melting point of the solder, and the texture becomes brittle, and it is easy to appear small cracks during cooling, which is not suitable for sealing, so its use is greatly limited.
3. Mixing pot
The melting point of the doped solder increases and can be used as a high melting point solder. Because the thermoelectric motive force of the pot zinc solder (82.5%, zinc 17.5%) is small, it can be used in welding measuring instruments. At the same time, this solder can also be used to weld aluminum. Bangle-zinc-silver (3%) solder can be used as a high temperature soft solder. However, due to the existence of public nuisance problems, the use of this solder is becoming less and less.

What is the Basic of No Oxidized Solder?
Solder components often contain oxides of tin and lead, which, like other non-metallic impurities, have been neglected in the past. Recently, it was found that these oxide residues were included in the solder, forming many small grains with impurities as the center, which seriously affected the welding quality. Oxidation free solder (tin-lead series solder) is a coarse pure alloy, which is very important for highly reliable solder in terms of ultra-miniaturization and miniaturization of components. This type of solder is manufactured by vacuum melting. This type of solder is much more diffusible than the solder melted in the air. In particular, the solder made of tin and lead after vacuum melting respectively, and then melted in vacuum according to the proportion of the solder, its diffusion is 16% ~24% higher than that of the solder melted in air.
What is the Basic of Lead-free solder?
In recent years, with the strengthening of people's awareness of environmental protection, as well as the inherent toxicity of lead metal (the destruction of the human nervous system), the use of lead in the electronic assembly industry has been put on the issue. The European Union's Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) group has called for an end to the use of lead-based materials in the electronic assembly industry by 2006. The National Electronics Manufacturing Association (NEMI) has specifically implemented a program called "NEMI's Lead-Free Welding Program" to systematically study the use of lead-free assembly in the electronics industry.
As the world's largest electronic assembly industrial country, Japan's major consumer electronics companies have committed to complete delivery of lead-free electronic assembly as soon as possible, which makes the research of lead-free solder imminent. As a developing country in high speed, the scale of micro-industrial is also expanding day by day.
In order to determine the best alternative composition to further enhance the market competitiveness of solder manufacturers and customers, IPC(International Electronic Industry Connection Association) together with the world's leading material manufacturers to set up the "solder Product Value Council" (SolderProduct Value Council). The properties and reliability of each component are studied and compared together, in order to be the best substitute for tin lead co-alloy.
1. Lead-free solder should have the performance
According to the environmental protection requirements and industrial practical applications, the search for a comprehensive replacement of Sn-P in the electronic assembly industry must meet the following requirements:

(1) The melting point of the low-melting material must be low enough to avoid thermal damage to the organic electronic components, but must also be able to meet the existing assembly process with good mechanical properties.
(2) Wet ability only when the solder and the base metal have good wetting can a reliable connection be formed
(3) Availability: The metal used in lead-free solder must be non-toxic and available in abundance.
(4) Price: The price of the metal used in the solder is a factor, as is the additional cost of changing the assembly line with the new solder
2. Research status of lead-free solder According to the above requirements, almost all the research of lead-free solder is developed with Sn as the main component, and binary, ternary or even quaternary eutectic alloy systems are formed by adding In, Ag, Bi, Zn, Cu and AI. The main reason is that the eutectic alloy has a low melting point. Table 10-5 shows the eutectic reaction temperature and eutectic composition of several binary eutectic solders. It can be seen that SNin alloy has the lowest melting point, while Sn-Au alloy is suitable for high temperature. However, recent studies mainly focus on Sn-Ag and Sn-Zn series, Sb and I are excluded due to toxicity, Bi and Au are too expensive to be suitable for industrial use.
The high melting point of the Sn-Ag system can be reduced by the addition of a small number of other components, and the inherent susceptibility to oxidation of the Zn system can be avoided by inert gas protection installation. A large number of ternary or even quaternary Sn base alloys have been studied in order to obtain better connection properties. The following will be summarized from the existing lead-free solder melting point, connection interface wettability, intermetallic compound phase precipitation, mechanical properties, corrosion properties and composition ratio.
Reference
He Wei, PCB Basic Electrical Information Science and Technology, China Machine Press,203-206
Industry Category











