What Is Induction Cooker Pcb?-3 Types
By: 08/29/2023 13:59
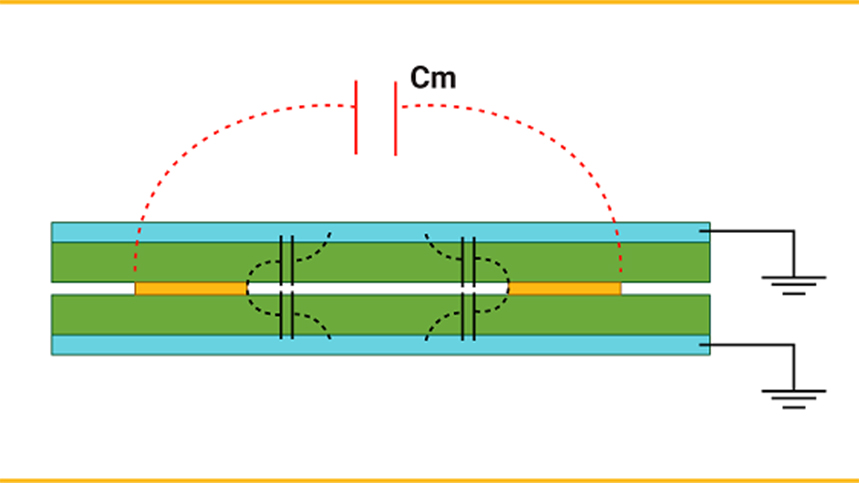
This article aims to delve into the relevant issues concerning the circuit board of an induction cooker, including its definition, classification, manufacturing process, and application areas. Through the review and assessment of existing research, it unveils the essential elements and functions of the induction cooker circuit board. Additionally, this article discusses the application scenarios of the induction cooker circuit board across various domains and provides suggestions and prospects for future research.
what is induction cooker?
Induction cookers have become increasingly popular kitchen appliances in modern households. They utilize electromagnetic induction principles to heat food, bringing great convenience to people's lives. The circuit board of an induction cooker, as a core component, is responsible for receiving and processing various operational instructions to ensure the proper functioning of the induction cooker. Therefore, research and improvement of the induction cooker circuit board are of significant importance.
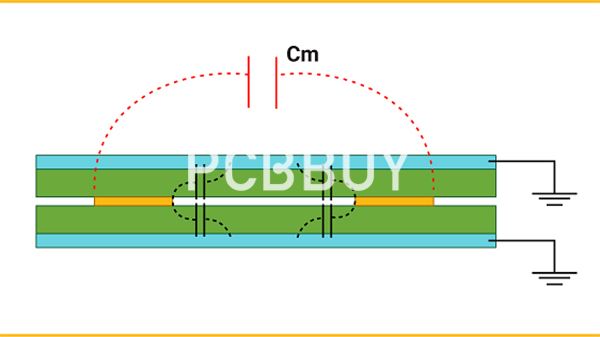
Firstly, the primary function of the induction cooker circuit board is to receive operational instructions and process feedback information. Users input commands through the control panel, which the circuit board receives and processes. It then controls the heating time and power level of the induction cooker, achieving the heating and cooking of food. The circuit board also collects data from various sensors such as temperature and water level, and uses this information for feedback control, ensuring the normal operation of the induction cooker.
Secondly, there are various types and characteristics of induction cooker circuit boards. Common circuit boards include microcontrollers, LCD driver boards, and power driver boards. The microcontroller serves as the core control component, responsible for handling operational instructions and sensor data. The LCD driver board drives the display screen to show the working status and menu information of the induction cooker. The power driver board controls the power output of the cooker to ensure effective heating. Different types of circuit boards have distinct features and functions, requiring selection and matching based on practical needs.
Furthermore, induction cooker circuit boards can experience malfunctions during use. Common issues include unresponsive buttons, dim displays, and unstable heating. These malfunctions may stem from electronic component failures, poor connections, or programming errors on the circuit board. Depending on the root causes of different malfunctions, corresponding diagnostics and repairs are necessary.
Lastly, maintenance and upkeep of the induction cooker circuit board are essential. Users should take precautions against moisture, corrosion, and high temperatures during everyday use to prevent damage to the circuit board. Regular cleaning and maintenance should also be conducted to ensure the proper operation of the circuit board. Timely handling is required if malfunctions are detected.
what is induction cooker pcb?
The induction cooker circuit board is a core component of the induction cooker, and its functionality and design directly impact the performance and safety of the induction cooker.
The induction cooker circuit board is primarily composed of various electronic components, including power transistors, rectifier bridges, power modules, induction cooker sensors, capacitors, electronic switches, and more. Through specific layouts and connections, these components realize the various functions of the induction cooker.
Among them, power transistors are crucial elements in the induction cooker circuit board, responsible for controlling the power output of the induction cooker. These power transistors use high reverse voltage, high current endurance, and high impact voltage endurance, enabling efficient energy conversion and control to ensure stability and efficiency during the heating process. Rectifier bridges convert alternating current into direct current, providing a stable power supply voltage for the induction cooker. Power modules transform direct voltage into various low voltages to meet the operational requirements of different components in the induction cooker.
Induction cooker sensors are used to detect the temperature of the cooking surface and the presence of pots and pans. Common sensors include thermistors and magnetic sensors. Thermistors are employed to detect the cooking surface temperature; when the temperature becomes too high, the circuit board controls the induction cooker to stop heating, ensuring the safety of the equipment and users. Magnetic sensors detect the material and size of the cookware; when cookware is not detected, the circuit board also controls the induction cooker to stop heating. Capacitors and electronic switches are utilized for auxiliary functions such as filtering, energy storage, and switch control.
Styles of induction cooker pcb
Induction cooker circuit boards can be classified based on various factors, with common classifications including imported boards, domestically produced boards, and printed boards. These classifications differ in terms of performance, price, and reliability.

Imported boards generally offer higher performance and quality, featuring increased stability and reliability, albeit at a higher price point. Printed boards are the most budget-friendly option, suitable for low-cost and low-power induction cooker products.
When selecting an induction cooker circuit board, it's essential to consider your specific needs and usage environment. For high-end products, opting for imported boards with high stability and reliability is recommended. For mid-range and budget products, domestically produced boards offer a good balance between performance, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Printed boards are a suitable choice for low-cost and low-power induction cooker products, as they come at a lower price point while still meeting performance requirements.
induction cooker pcb technology
The manufacturing process of an induction cooker circuit board involves multiple stages, including PCB design, graphic processing, board material cutting, drilling, component placement, and soldering. Each of these stages requires precise operations and quality control to ensure the quality and performance of the induction cooker circuit board.
During the PCB design phase, layout and routing are conducted based on the circuit design and functional requirements of the induction cooker. Rational component layout and circuit design can enhance the stability and performance of the circuit board while reducing potential risk of malfunctions. Graphic processing involves transforming the designed circuit board graphics into the actual board layout, requiring accuracy and completeness of the graphics.
Board material cutting and drilling are critical steps in circuit board fabrication, demanding specialized equipment and techniques to ensure precise dimensions and hole locations. Component placement involves the process of positioning electronic components onto the circuit board according to the design specifications, carried out either through automation or manual methods. Accuracy of component placement in terms of position and orientation is crucial.
Soldering is a vital step in connecting components to the circuit board, necessitating appropriate soldering methods and techniques to ensure the quality and reliability of solder joints. The quality of soldering directly impacts the overall quality and performance of the circuit board, hence meticulous control over the soldering process and quality is essential.
induction cooker pcb used for
The electromagnetic stove circuit board is an essential electronic component widely employed in various domains including households, offices, and industries. The following analysis illustrates the application scenarios of the electromagnetic stove circuit board across different fields.

Firstly, in households, the electromagnetic stove has become a prevalent kitchen appliance. Compared to traditional gas stoves and electric cookers, electromagnetic stoves offer advantages like rapid heating and energy efficiency. Using an electromagnetic stove allows rapid heating of cookware to high temperatures, facilitating swift heat transfer for enhanced cooking efficiency. Additionally, the heat energy generated by the electromagnetic stove can be effectively stored within the cookware materials, enabling intelligent and efficient heat utilization. At home, electromagnetic stoves are utilized for boiling, steaming, stir-frying, and various cooking methods, providing convenience in daily life.
Secondly, in office environments, electromagnetic stoves offer convenient hot food preparation experiences for employees. Offices may lack dedicated cooking areas or have limited space for large kitchen equipment. Due to their compact size, electromagnetic stoves can be placed on desks or in separate kitchen areas, offering straightforward and speedy operation for easy hot food cooking. Employees can use electromagnetic stoves to cook simple dishes according to their taste and preferences, enhancing the convenience and comfort of office life.
In the industrial sector, electromagnetic stoves find extensive applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical engineering, and more. In food processing industries, electromagnetic stoves are employed to process various food ingredients such as meat, vegetables, and soy products. The high-temperature heating of electromagnetic stoves allows rapid cooking and stewing of food ingredients, boosting production efficiency and product quality. In the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, electromagnetic stoves are used to heat chemical reagents within reaction vessels, promoting chemical reactions and improving production efficiency and quality stability.
Furthermore, electromagnetic stove circuit boards also find applications in aerospace, automotive, and other fields. In the aerospace sector, electromagnetic stoves are utilized for heating and cooking food, offering high-quality inflight meal services. In the automotive sector, electromagnetic stoves can be used to heat and maintain car battery packs, enhancing the range and safety of electric vehicles.
In summary, the electromagnetic stove circuit board finds extensive applications in various domains including households, offices, and industries, offering advantages such as rapid heating and energy efficiency. With the continuous advancement of technology and the improvement of people's living standards, the application prospects of electromagnetic stove circuit boards are expected to become even broader.
Industry Category











