What Is the Process of Rapid PCB Manufacturing?
By:PCBBUY 06/25/2022 10:25
The manufacturing process of a PCB is pretty extensive. Whether you a PCB manufacturer or others, steps are crucial to the development of the board. Because each step is so critical to the process, let’s take a close look at the manufacturing process of a PCB. And we are talking about the manufacturing process in the content below.
If you want to order PCB product, please check and custom your order online.
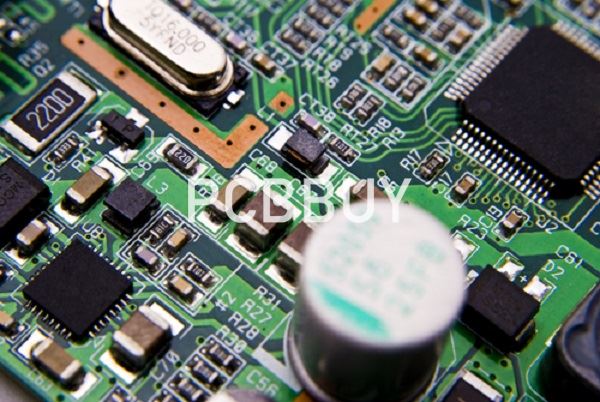

What are the basic PCB design rules?
Material rules for PCB design
Consider during the layout phase the materials and components you plan to use for your board. You’ll first need to make sure the desired items are accessible. Some materials and parts are hard to find, while others are so expensive they’re cost-prohibitive. Different components and materials may also come with different designs needs.
Take time to ensure you’ve chosen the optimal materials and components for your board, and also that you’ve designed a board that plays to those items’ strengths.
The routing guidelines for PCB design
Printed circuit board design rules and PCB layout guidelines become more complex as the number of layers in your stackup increases. Your routing strategy will require alternating horizontal and vertical traces in alternating layers unless you separate each signal layer with a reference plane. In very complex boards for specialized applications, many of the commonly-touted PCB best practices may no longer apply, and you'll need to follow PCB design guidelines that are particular to your application.
Defining net widths
Your printed circuit board design will likely require different nets that will carry a wide range of currents, which will dictate the required net width. With this basic requirement in mind, it’s recommended to provide a 0.010” width for low current analog and digital signals. Printed circuit board traces that carry more than 0.3 A should be wider. Here’s a free Trace Width Calculator that makes this process easy. You can also use this calculation (based on IPC-2152) to determine your PCB trace width.
What are the common surface treatment processes of PCB?
Hot air leveling
Hot air leveling, also known as hot air solder leveling, is a process of applying molten tin-lead solder to the surface of the PCB and leveling it with heated compressed air to form a coating that is both resistant to copper oxidation and provides good solderability. When the hot air is leveled, the solder and copper form a copper-tin intermetallic compound at the junction. The thickness of the solder that protects the copper surface is approximately 1-2 mils.
The PCB is immersed in molten solder during hot air leveling; the air knife blows liquid solder before the solder solidifies; the air knife minimizes the meniscus of the solder on the copper surface and prevents solder bridging. Hot air leveling is divided into vertical type and horizontal type. It is generally considered that the horizontal type is better, mainly because the horizontal hot air leveling coating is relatively uniform and can realize automatic production. The general process of the hot air leveling process is: micro-etching→preheating→coating flux→spraying→cleaning.
What are main PCB heat dissipation techniques?
Identifying thermal and high-current traces
To fabricate a thermally stable PCB, thermal effects must be studied during the designing phase itself. The first step in thermal design is to identify the hotspots. Thermal modeling or thermal simulation techniques are used to find hotspots. Also, current flow analysis must be done along with it, because high-current traces cause heat generation.
The proper geometrical arrangement of components and high-current traces enables even distribution of heat. High-current traces must be routed away from thermally sensitive components such as sensors and Op-amps.
Use wider traces for reduce heat
Copper traces that conduct high currents build up heat. Therefore, it is important to increase the width of the trace to maximize heat dissipation to the air. Doing so also reduces the thermal resistance of the trace and reduces heat spots.
PCB thermal vias design
You can turn a PCB into an onboard heat sink by incorporating thermal via arrays over copper-filled areas, as shown above. The idea behind doing so is to have heat flowing from components to the copper area and dissipating through the air from the vias. Usually, thermal via arrays are used for power management modules and components with thermal pads.
When implementing thermal via arrays, remember that it needs to have a reasonably large diameter, in the region of 0.1 mm, for the heat to be dissipated effectively. Also, ensure the vias are not thermal-relief pads but padded holes that are connected to the copper area at all sides. Increasing the number of thermal vias further helps with heat dissipation.
Proper material to help heat dissipation
There are materials other than epoxy resins that are better suited to dissipate disproportionate levels of heat such as polyimides or metal cores. If these materials are used, the decision has to be made upfront as these materials will have very different electrical characteristics, completely changing the structure of the design.
Industry Category











