What Role Does PCB Copper Balance Play in PCB Design and Manufacturing?
By:PCBBUY 03/26/2025 15:39

Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing the foundation for interconnecting and supporting components. Among the many critical design considerations, copper balance is an essential factor that significantly impacts PCB performance, reliability, and manufacturability. This article delves into the intricate role of PCB copper balance, exploring its principles, practical applications, and challenges in PCB design and manufacturing.
Understanding Copper Balance in PCBs
What Is Copper Balance?
Copper balance refers to the equal distribution of copper on a PCB layer to prevent uneven stresses during the manufacturing process. PCBs consist of alternating layers of copper and insulating material, and maintaining a balanced copper distribution ensures mechanical stability, thermal management, and proper functioning.
Unbalanced copper distribution can result in the following:
-
Warping and Bowing: Uneven stresses during lamination.
-
Electrical Interference: Irregular signal paths and impedance mismatch.
-
Manufacturing Challenges: Difficulty in etching and layer alignment.

The Principles of Copper Balancing
Copper balance is achieved through:
-
Layer Symmetry: Ensuring that copper areas on the top and bottom layers are evenly distributed.
-
Pattern Fillers: Adding dummy copper areas in low-density regions.
-
Weight Balancing: Maintaining uniform copper weight across all layers.
Importance of Copper Balance
1. Mechanical Stability
Copper imbalance can cause mechanical deformation during the lamination process. Unequal copper areas lead to varying thermal expansion rates, resulting in warping or bowing.
Key Data
|
Copper Imbalance (%) |
Warping Angle (Degrees) |
|
10% |
5° |
|
20% |
15° |
|
30% |
30° |
This table illustrates how increased copper imbalance correlates with higher warping, compromising the PCB’s structural integrity.
2. Thermal Management
Copper plays a crucial role in dissipating heat generated by electronic components. Imbalanced copper distribution can create hotspots and thermal gradients.
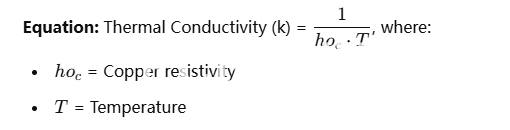
where:
-
hoc ho_c = Copper resistivity
-
TT = Temperature
Balanced copper layers ensure even heat distribution, minimizing thermal stress.
3. Electrical Performance
Copper imbalance impacts electrical performance by causing signal integrity issues. Uneven copper areas can lead to:
-
Impedance mismatch.
-
Increased electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Using electromagnetic field simulation tools, designers can predict and optimize copper distribution to maintain electrical performance.

Copper Balance in the Manufacturing Process
1. Lamination
The lamination process involves bonding layers under heat and pressure. Copper imbalance results in differential expansion rates, leading to misalignment or delamination.
Key Chemical Equation in Lamination:
Epoxy resin curing:
C6H6O3+CH2O→C6H6O3CH2
The curing process is sensitive to thermal and mechanical stresses caused by uneven copper.
2. Etching
During etching, unbalanced copper can lead to over-etching or under-etching, affecting the circuit’s functionality. Dummy copper areas mitigate this issue by ensuring uniform etchant flow.
Etching Rate Comparison:
|
Copper Area Coverage (%) |
Etching Time (Seconds) |
|
30% |
40 |
|
60% |
70 |
|
90% |
100 |
3. Plating
Electroplating relies on consistent current distribution. Uneven copper areas create resistance variations, leading to non-uniform plating thickness.
Techniques to Achieve Copper Balance
1. Dummy Copper Fillers
Dummy copper fillers are non-functional copper areas added to balance the overall copper distribution. These areas reduce mechanical and thermal stress without affecting circuit performance.
2. Cross-Hatching
Cross-hatching involves using a grid pattern for copper areas, balancing weight while reducing parasitic capacitance. This technique is particularly useful for RF and high-speed PCBs.
3. Simulation Tools
Advanced CAD tools simulate copper distribution and identify imbalance areas. Tools like Altium Designer and KiCAD allow designers to visualize and optimize copper balance.

Real-World Applications of Copper Balance
Case Study: High-Speed PCBs
High-speed PCBs require precise impedance control, which is directly influenced by copper balance. Designers use microstrip and stripline configurations to maintain uniform signal paths.
Impedance Formula:

Balanced copper ensures consistent Z0Z_0, minimizing signal reflection and attenuation.
Automotive PCBs
Automotive PCBs operate in harsh environments, requiring robust thermal and mechanical properties. Copper balance enhances reliability and prolongs lifespan.
Challenges in Copper Balance
1. Design Complexity
Achieving copper balance becomes challenging as PCBs integrate more components and layers. Designers must balance functionality and manufacturability.
2. Manufacturing Tolerances
Small variations in etching or plating processes can disrupt copper balance, especially in high-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs.
3. Cost Considerations
Implementing copper balancing techniques may increase design and manufacturing costs, particularly for low-budget projects.
Conclusion
Copper balance is a critical aspect of PCB design and manufacturing, directly impacting mechanical stability, thermal management, and electrical performance. By employing techniques such as dummy copper fillers, cross-hatching, and simulation tools, designers can achieve optimal copper distribution. Although challenges like design complexity and cost considerations exist, the long-term benefits of balanced copper far outweigh the drawbacks.
A comprehensive understanding of copper balance not only enhances PCB reliability but also sets the foundation for advanced electronic applications, from consumer devices to automotive systems.
References
-
IPC-2221 Standard for PCB Design.
-
Altium Designer Documentation.
-
Fundamentals of Microelectronics by Behzad Razavi.
-
"Thermal Management in PCBs, IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging, and Manufacturing Technology.
-
Advanced Circuitry International, Copper Balance Techniques in PCB Fabrication.
Industry Category











