What is Signal Integrity Analysis in PCB Design?
By:PCBBUY 04/15/2022 09:51
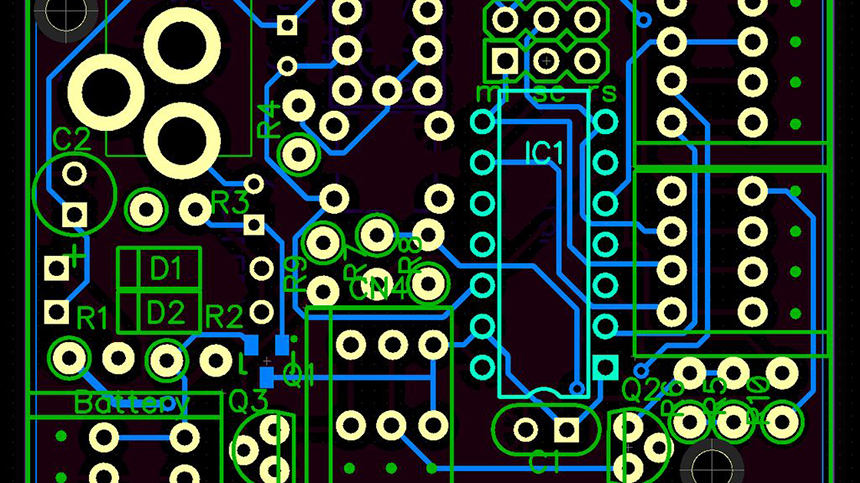
Signal Integrity (SI) signifies the signal’s ability to propagate without distortion. Signal integrity is nothing but the quality of the signal passing through a transmission line. It gives the measurement of the amount of signal degradation when the signal travels from the driver to the receiver. This problem is not a major concern at lower frequencies but is an important factor to consider when a PCB operates at a higher speed and a high-frequency (> 50MHz). In the high-frequency regime, both digital and analog aspects of the signal need to be taken care of.
If you are curious about the signal integrity analysis in PCB design, please check and read the content for more information in this passage.

What are the problems of signal integrity in PCB design?
The effects of interference on the operation of electronic devices can be pretty dramatic. For years, flight attendants urged us to shut down our cell phones or we were annoyed with radios that produced static instead of clear audio. Some older computers even radiated so much EMI that they were eventually taken off the market. However, the majority of problems caused by poor signal integrity are usually more subtle than that—there might be the occasional glitch in performance, data might get dropped, or the device may even fail to operate in extreme cases. All of these issues can often be traced back to signal integrity problems.
As signal speeds increase in our electronics, they are more susceptible to a variety of aggressive interferences. These can include signal reflections due to impedance mismatches, ground bounce, and crosstalk. If the circuit board is not specifically laid out to counter these problems, the signal degradation may continue until it no longer works as designed. Additionally, the circuit board must be designed so that it doesn’t create signal integrity problems for its own circuitry or nearby electronics. Before we look at how to design for these problems, let's first take a look at some critical signal integrity fundamentals.
What are the issues of PCB signal integrity?
PCB signal integrity issues mainly include signal reflection, crosstalk, signal delay, and timing errors.
Reflection
When the signal is transmitted on the transmission line, when the characteristic impedance of the transmission line on the high-speed PCB does not match the source impedance or load impedance of the signal, the signal will be reflected, causing the signal waveform to overshoot, undershoot and the ringing phenomenon caused by it. Overshoot refers to the first peak (or bottom) of the signal transition. It is an additional voltage effect above the power supply level or below the reference ground level. Undershoot refers to the signal jump change to the next valley (or peak). Excessive overshoot voltage often impacts the device for a long period of time, causing damage to the device. Undershoot will reduce the noise margin. Ringing increases the time required for signal stabilization, which affects system timing.
Crosstalk
In PCB, crosstalk refers to the undesired noise interference caused by the electromagnetic energy through the mutual capacitance and mutual inductance coupling to the adjacent transmission line when the signal propagates on the transmission line. It is caused by interaction of different structures of the electromagnetic field in the same area. Mutual capacitance causes coupling current, which is called capacitive crosstalk; while mutual inductance causes coupling voltage, which is called inductive crosstalk. On the PCB, crosstalk is related to trace length, signal line spacing, and the condition of the reference ground plane.
Signal delay and timing error
The signal is transmitted at a limited speed on the wires of the PCB, and the signal is sent from the driver to the receiver, with a transmission delay in between. Excessive signal delays or mismatched signal delays can lead to timing errors and disrupted logic device functionality.
High-speed digital system design analysis based on signal integrity analysis can not only effectively improve product performance, but also shorten product development cycles and reduce development costs. With the development of digital systems toward high speed and high density, it is extremely urgent and necessary to master this design weapon. With the continuous improvement and improvement of signal integrity analysis models and calculation analysis algorithms, digital system design methods that use signal integrity for computer design and analysis will be widely and comprehensively applied.
What are the applications of signal integrity in PCB layout?
In the process of PCB design, a lot of design rules have been summarized based on signal integrity theory. With reference of these PCB design rules, signal integrity can be obtained better. In the process of PCB design, design information has to be known in detail, including:
· Component layout position, whether there are special requirements on components with large power and heat dissipation on chip components.
· Classification of signals, speed rate and transmission direction and impedance matching requirement.
· Signal driving capacity, key signal and protection measures.
· Types of power, ground, noise limit requirement of power and ground, setting of power plane and ground plane and division.
· Type and speed rate of clock lines, source of clock lines, direction, delay requirement of clock and maximum routing requirement.
Industry Category











