Fr4 material in PCB
By:PCBBUY 06/09/2021 17:29
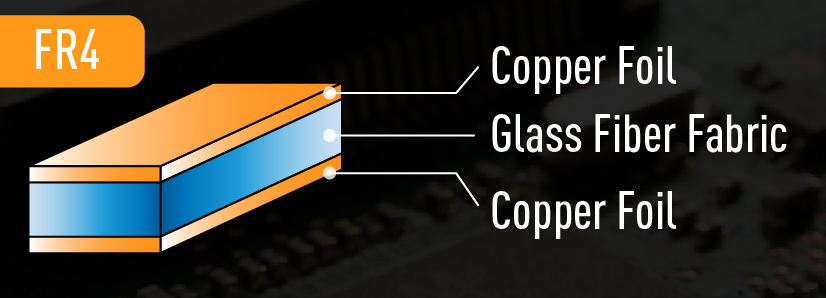
FR4, also written as FR-4, is both a name and a rating. FR4 is the backbone material upon which most rigid circuit boards are built. The name also functions as a grade used to rate epoxy laminate sheets. The “FR” in the name stands for flame retardant, while the 4 differentiates the material from others of the same class. The designation essentially indicates the base quality of a laminate sheet, meaning a variety of sheet materials and designs fall under the FR4 rating.
FR4 sheets are widely popular among electrical engineers and designers as a PCB base material. The low cost and versatility of the material, as well as its wealth of beneficial physical properties, accounts for that popularity. FR4 sheets are electrical insulators with high dielectric strength. They also feature a high strength-to-weight ratio and are lightweight and resistant to moisture. Add this to their relative temperature resistance, and FR4 can perform well in most environmental conditions.
Let’s check the content below for more detailed knowledge of Fr4 material in PCB.

What is the connection of Fr4 in PCB?
Within a PCB, FR4 forms the primary insulating backbone. This is the base upon which the manufacturing company builds the circuit. Once prepared, the FR4 board is laminated with one or more layers of copper foil using heat and adhesive. This copper forms the circuits in the finished product and may cover one or both sides, depending on the design of the board.
Complex PCBs may use more than one side or even layer the circuit board to produce more sophisticated circuits. From here, the circuits are drawn and etched out before being covered with a solder mask layer, preparing the board for the final silkscreen layer and the subsequent soldering process.
How to select Fr4 thickness?
When ordering a laminate board for a PCB project, the designer or electrical engineer must specify the FR4 PCB thickness. This is measured in inch-based units, such as the thousandth of an inch, or thou, or millimeters, depending on which is most appropriate for the setting. The thickness of a sheet of FR4 ranges widely depending on the needs of the project, but it tends to range from ten thou to three inches.
While board thickness may not seem like a significant factor in the design of a PCB, in reality, it is an essential feature. Board thickness affects several aspects of the board’s functionality, which is why several factors are considered in determining the thickness of a board for design. These include the following.
Space: thinner may be better
If space concerns the designer, a thinner FR4 board tends to be preferable. This is a predominant factor for the manufacture of smaller devices, like USB connectors and many Bluetooth accessories. Even for larger projects, smaller FR4 PCBs tend to be favored to save space within the device.
Connections: the wrong one could result in damage
A two-sided PCB design requires an edge connector to join the two sides. This can be a major limiting factor for the final size of the PCB since PCB edge connectors only fit a particular set of PCB thicknesses. The mating portion of a connector has to fit snugly on the side of the PCB, or else risk slippage or damage to the PCB. This is one of the primary reasons why circuit design comes before choosing materials for the circuit.
Impedance matching: essential to maintaining board function
Every multi-layered board acts as a capacitor on adjacent layers. This is why the thickness of this board is so important — the thickness of the PCB FR4 determines the thickness of the dielectric, which in turn affects the value of the capacitance.
This is an especially key factor for some high-frequency PCBs, such as RF and microwave designs. High-frequency designs focus on impedance matching as an essential component to maintain optimal board function, so getting the right capacitance for each layer is crucial.
Flexibility: depends on the application
Thinner boards can flex in some capacity. While an unusual trait, flexibility can be a positive or negative feature, depending on the application.
More flexible boards tend to be preferable in some applications where the product is regularly stressed or flexed. For example, those using boards for medical and automotive applications often prefer flexible boards due to the constant stress and flexing to which these PCBs are often subjected.
However, flexibility can be a detriment to the PCB manufacturing process, resulting in serious problems later in assembly. When handled by a machine, a more flexible board may flex when dealt with by a soldering machine, causing the component to be soldered at an angle. Additionally, this flexing has the potential to break freshly placed components and connections already on the board.
Design requirements: intended use impacts Fr4 thickness
Thin boards aren’t preferable in all cases, primarily due to the limitations thin boards put on PCB plans. Thin FR4 boards can’t feasibly feature grooves, and they can’t be too large without risking fracture. Thicker boards, however, can accomplish both. Always account for this when weighing options between FR4 thicknesses.
Components compatibility: may work with a small range
The thickness of a board can also affect the compatibility of components with the board. Just like edge connectors, many components work with a small range of board thicknesses. This is especially true for some through-hole components, for example.
Weight: lighter products may be more attractive
The thickness of an FR4 board will, logically, affect the weight of the final PCB. While weight is less of an issue in some applications, it is often a consideration in consumer electronics. Lighter PCBs make for lighter products, which makes them cheaper to ship and, in some cases, more attractive to consumers.
Industry Category











