What is PCB Wave Soldering and What Is the Function?
By:PCBBUY 02/14/2022 09:57
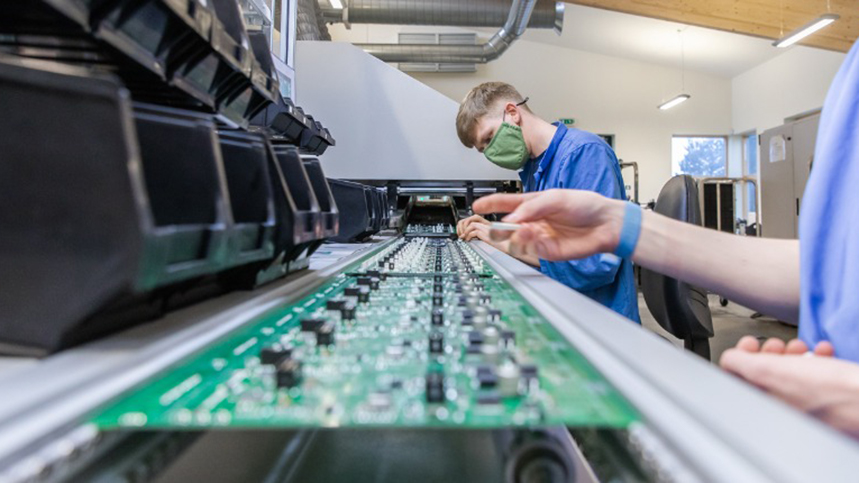

In the market, you will encounter many kinds of wave soldering machines. You can buy lead wave solder machines or lead-free wave solder machines. It is all up to you. However, the main principles and fundamental parts of all of these machines are alike. A conveyor is an essential part that is used during this process. It takes printed circuit boards via various zones.
Are you going to learn more information about PCB wave soldering? If you are looking for more information about PCB wave soldering, please check and read the content below in this passage.

What are the common problems of PCB wave soldering?
Wave soldering is a large-scale soldering process by which electronic components are soldered to a printed circuit board (PCB) to form an electronic assembly. The name is derived from the use of waves of molten solder to attach metal components to the PCB. The process uses a tank to hold a quantity of molten solder; the components are inserted into or placed on the PCB and the loaded PCB is passed across a pumped wave or waterfall of solder.
The solder wets the exposed metallic areas of the board (those not protected with solder mask, a protective coating that prevents the solder from bridging between connections), creating a reliable mechanical and electrical connection. The process is much faster and can create a higher quality product than manual soldering of components.
Wave soldering is used for both through-hole printed circuit assemblies, and surface mount. In the latter case, the components are glued by the placement equipment onto the printed circuit board surface before being run through the molten solder wave.
What is the preparation of PCB wave soldering?
In order that a electronics printed circuit board may be successfully processing using a wave soldering machine, it is necessary that it is designed and manufactured in the correct manner.

Solder resist layer: The first is standard practice when designing boards these days. A solder resist or solder mask layer is included in the PCB design, and this adds a layer of "varnish" like material to the board to which the solder will not adhere. Only those areas where the solder is required are left exposed. This solder resist is most commonly green on colour.
Pad spacing: The second main precaution is to ensure that there is sufficient spacing between the solder pads requiring soldering. If they are too close then there is the possibility that the solder may bridge the two pads causing a short circuit.
In view of the way that wave soldering works, where the solder wave is caused by the solder flowing out of the reservoir tank, and the board passes over it, the spacing requirements are dependent upon the direction of the board relative to the solder flow. Pads that are spaced apart in the direction of the solder flow should have a greater spacing than those that are spaced at right angles to the solder flow. This is because it is much easier for solder bridges to occur in the direction of the solder flow.
What are the defects of PCB wave soldering?
Insufficient hole fill is a problem that occurs on printed circuit boards with pre-drilled holes for components to be mounted onto the board. Essentially, insufficient hole fill occurs when an inadequate amount of solder has filled the holes drilled for the components, meaning solder won’t stick to the circuit board once it cools. There are several reasons for insufficient hole fill:
The flux was applied incorrectly and did not penetrate through the board, meaning the solder was not activated and could not bind the components properly.
The temperature of the top side of the board isn’t high enough to turn solder molten so it can rise through the holes.
There was not enough of the board in the wave of the solder. If not enough of the board makes contact with the wave, too little solder is pushed up into the through-holes.
The best way to fix these issues is to run through another series of pre-solder checks. Check the type of flux you’re using, and make sure there’s a sufficient volume of it to cover the entire PCB.
This step will also help with the second problem: insufficient pre-heat. Older flows to heat, the solder won’t flow as well if your PCB’s through-holes aren’t at the correct temperature
Since solder flows to heat, the solder won’t flow as well if your PCB’s through-holes aren’t at the correct temperature. While the “right” temperature depends on your company’s operating standards, the general rule of thumb is between 300 and 340 degrees Fahrenheit, or roughly 150 to 170 degrees Celsius.
The whole assembly needs to reach this temperature before the board makes contact with the wave. If you’re not sure whether your through-holes are reaching the correct temperature, take a profile of the wave-solder process — it should look either exactly alike or very similar to your board’s reflow processes.
Industry Category











