PCB laminate
By:PCBBUY 05/20/2021 17:37
PCB, also known as etched wiring board, is a structure used to connect and support electronic components through conductive pathways. These pathways are etched from copper sheets that are laminated into a substrate that does not conduct the signal.
Understanding the different types of laminate for a printed circuit board is crucial for the design and development process your PCB manufacturer will go through. The type of laminate you choose will determine the stability and overall performance of your PCB board.
The laminate of the PCB is what holds the layers together. Traditionally, there are four layers that make up the board: Substrate, Copper, Soldermask, and Silkscreen (from bottom to top). The laminates are developed by curing under pressure and temperatures of cloth using thermoset resin to create the final piece of uniform thickness.
When you see a type of laminate written out, it typically will look like this: FR-4 (with FR-4 being the most common material used). These numbers and letters are the characteristics of the laminate produced. Some of the important characteristics include: fire retardant, dielectric constant, loss factor, tensile strength, shear strength, glass transition temperature, and how much thickness changes with temperature (the Z-axis expansion coefficient).

What are the types of PCB laminate?
The following list is comprised of the different types of PCB laminates and the PCB materials needed, starting with the most common ones. The designation of a laminate comes from the resin used.
FR-4
What makes FR-4 the most commonly used laminate is how it performs across all characteristics. This material has a good strength-to-weight ratio, is flame resistant, which improves its reliability, and when there is an increased temperature, the material’s mechanical, electrical, and physical properties stay maintained.
High-Performance FR-4
You would use a high-performance FR-4 laminate when dealing with multi-layered PCBs. It has a high-reliability level due to the increased TG and is more suitable for high-frequency circuits because of its low dielectric properties.
High Tg Epoxy
For multilayer PCBs, the High Tg Epoxy is most suitable. The Tg is the vitrification temperature, similar to the melting point. The higher the number, the more rigid the board will be. A material with a high TG (over 170o C) has better heat, moisture, and chemical resistance, as well as better stability.
BT Epoxy
Most suitable for lead-free PCBs, the BT Epoxy laminate is known for having outstanding thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties. This laminate is commonly used for multilayer PCBs. It will also maintain bond strength at high temperatures.
Polyimide
This type of laminate produces extreme environmental stability. You would use the Polyimide laminate when working with high-density, flexible, rigid-flex circuit boards, and multilayer PCBs. It also produces high levels of thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties. A polyimide laminate is ideal for advanced applications, including military, aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
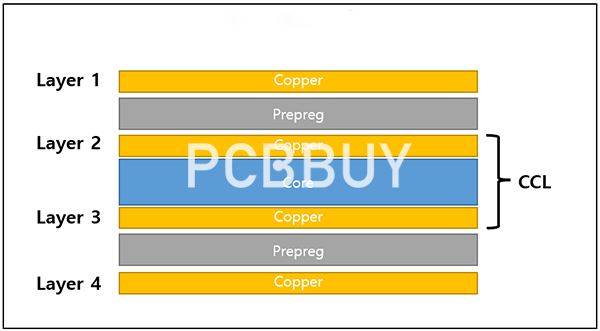
Copper Clad (CCL)
The Copper Clad laminate is made up of a glass fiber or wood pulp paper as the reinforcing material. You would typically use a CCL laminate for high-voltage circuits based on specific aspects, including appearance, size, electrical, physical, chemical, and environmental performance.
Teflon
The most commonly used material in high frequency applications. Teflon materials come in many different options, the easier materials to use in manufacturing are teflons with woven glass. There are several challenges with manufacturing teflon PCBs that causes issues with a conventional board shop.
What factors need to be considered during PCB laminates?
Now that you know the commonly used PCB laminates. Among the aforementioned types, which one should to choose to assemble the PCB? There are several factors to consider. A few of them include:
Dielectric constant
Loss factor
Thermal conductivity
Transition temperature
Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
Electrical performance
Ability to operate in varying thermal environments
Industry Category











