What is the Purpose of Reverse Engineering of PCB Manufacturing?
By:PCBBUY 01/04/2022 10:03

Reverse engineering a PCB is generally done because we want to copy the device or determine how it works. There are many reasons for doing this, both legitimate and not so legitimate. One reason for it is that the part is obsolete and must be updated and replaced. Sometimes the original design data has been lost. Another reason is that a company is trying to copy a competitor’s product.
Do you know the purpose of reverse engineering a PCB? In this passage, we are providing all the information about reverse engineering a PCB. If you are searching for more about reverse engineering, please check and read the content below.
Why we process reverse engineering on PCB?
PCB reverse engineering is a multilayered process that includes targeted PCB research, reverse analysis and PCB design technology reproduction. The process is also used to identify and obtain the design of a product’s functional and structural characteristics, as well as the processing flow. With this information, a company can produce products with similar functions and abilities — though businesses will make sure they’re not reproducing an exact replica of a reverse-engineered PCB.
Reverse engineering is primarily utilized to determine and analyze the design principles behind a product. It’s especially useful when a company can’t easily find design information on a specific product.
Since it is so difficult and complex, why do we still stick to it? We carry out reverse engineering of PCBs for a number of important reasons:
· Replace obsolete components on the board
· Reposition certain components
· Enhance the functionality of the PCB
· Analyze and reinforce the security requirements
The most common method of reverse engineering a PCB involves disassembling a sample PCB and then analyzing it. From this analysis, a company will create documentation about the sample PCB, which various team members can review. This documentation will often include information about how the product is designed and how it operates.
A company can then use the information they gather from a sample PCB to manufacture similar PCBs that may function better than their competitors’ offerings. Alongside reverse engineering’s ability to help companies analyze and outdo competitors’ products, it can also help businesses improve their own PCB offerings. For example, reverse engineering can help them enhance their boards’ functionality by spotting obsolete parts, security issues or poor designs.
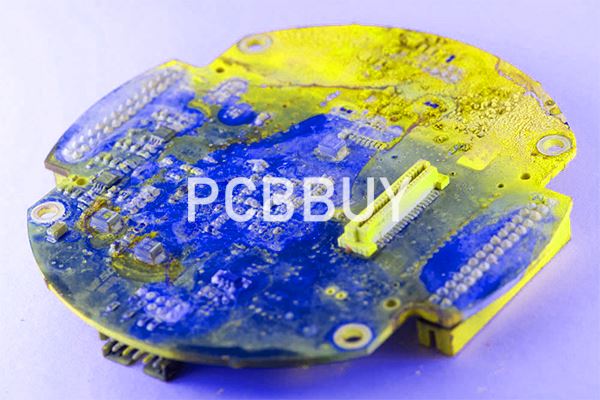

How to process reverse engineering on PCB?
Draw, Scan or Photograph the PCB for Image Prep
The first step to reverse engineering a PCB is drawing, scanning or taking a photograph of the PCB. If you take pictures of it, ensure you photograph both sides of the PCB. It’s also crucial to take pictures of it on a dark background. Since PCBs may have holes in them, you don’t want any background visible through these holes, as lighter backgrounds might look like copper. A dark background prevents any confusion about the PCB’s construction.
Another necessary step for properly photographing PCBs is to use a high-quality camera that can capture every detail. Digital cameras or smartphones usually suffice for this step. Additionally, you’ll want to ensure the PCB is well lit. Photographing or scanning images will involve a lengthy process afterward where you’ll need to perform color-switching or image editing. These steps are often required for complex layouts, as photographs and scans can pick up more complicated layouts.
Upload the Image
Once you’ve taken the pictures, you can then upload them to your reverse engineering program. Before you upload the imagery, manually crop the image so the photo only shows the PCB. There are multiple programs available online to help you edit any photos or scans and manipulate key PCB features.
For instance, you may want to use GIMP or Inkscape — both platforms are open-source, free graphics editors. Inkscape is a vector graphic editor. Dia is another free, open-source software solution for general-purpose diagramming. You may also want to consider using AutoTrace, a program that converts bitmap to vector graphics.
Construct the Layout
After uploading your images to your chosen reverse-engineering PCB program, you’ll then need to build a 3D layout of the PCB. A PCB’s layout shows how the system’s electromagnetic field distribution is arranged and how the circuits behave. It also represents other parts of a PCB that can’t be shown in a schematic, such as components, conductive elements, the arrangement of traces and each layer’s planes.
If you’re reverse engineering a simple PCB, you can often just scan a drawing of the PCB and upload it to AutoTrace — or a program like it — to build a layout. This type of program will take the bitmap image and convert it into a vector graphic, helping you obtain the PCB’s schematic quickly.
Industry Category











