Why FR4 is Used in PCB in the PCB Manufacturing Process?
By:PCBBUY 12/08/2021 09:11
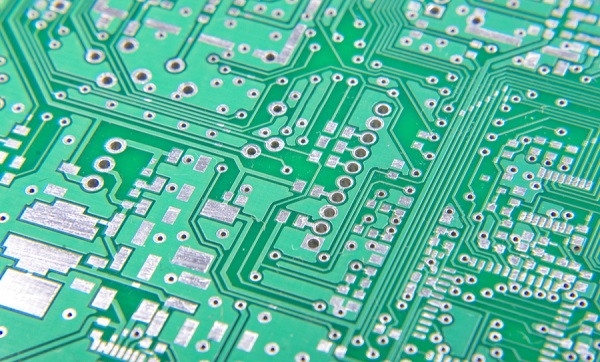
FR4 is the most common material grade that comprises fabricated circuit boards. ‘FR’ indicates the material is flame retardant and the ‘4’ indicates woven glass reinforced epoxy resin. Single or double-sided PCB structures consist of an FR4 core and top and bottom copper layers. Multilayer boards have additional prepreg layers between the center core and top and bottom copper layers.
The properties of FR4 may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer; however, it generally has favorable strength and water resistance attributes that support its widespread usage as an insulator for many electrical applications. It serves the same purpose in PCBs, namely to isolate adjacent copper planes and provide overall bending and flexural strength for the structure. FR4 is a good general purpose material for PCB fabrication; however, alternative materials are available. If you are going to learn more about FR4, please check and read the content below.
Why we use FR4 for PCB?
It is a PCB base material that comes as a fiberglass laminate sheet reinforced with epoxy resin. It is a common laminate substrate in printed circuit boards because of its sturdy nature and flame-retardant properties. As such, it is vital to provide circuit boards with the required insulation. FR4 boards have largely replaced the G-10 boards as much as the G-10 boards still find applications where thermal destruction proves key.
What are the properties of FR4 for PCB?
An FR4 material complies with the UL94V-0 standards when it comes to plastic in-flammability. The standards ensure that it cannot propagate fire and extinguishes it immediately after the material starts to burn.
Fr4 materials use bromine. The halogen chemical element is resistant to fire and thus valuable in providing the fire-retardant properties to FR-4. It also cannot absorb water, maintains the high mechanical strength, besides the incredible insulating capacity, especially in humid or dry environments.
FR4 material also has a high glass transition temperature of between 115 and 200 degrees Celsius. However, this depends on the methods of manufacturing and the resin types used. In most instances, the FR4 PCB will contain an FR4 sandwiched between two copper layer laminates.
The FR4 material can come as the standard FR4, the high TG FR-4, the high CTI FR-4, and FR4 without any laminated copper. A standard FR4 has a heat resistance of 140-a50 degrees Celsius, while a high TG FR4 possesses a glass transition value of 180 degrees Celsius. On the other hand, the high CTI FR4’s index exceeds 600V, and the FR4 devoid of laminated copper proves ideal for board support and insulating plates.
The thickness of the FR4 material plays a crucial role in diverse PCB applications. Therefore, picking the correct thickness should take into account the following.
· Compatibility of the FR4 thickness with components
· The need to save space on the board
· Flexibility and design
· The type of connections required
What are the laminations of FR4 for PCB?
FR4 has been used in the production of printed circuit boards for many years now. It’s inexpensive and provides adequate electrical insulation. However, when FR4 is used in high-speed applications the following problems may occur:
Insulating stability
Although FR4 is a great insulator, it has its limits when subjected to high power, voltage, or heat. If certain limits are exceeded, the materials’ insulating properties will deteriorate, and they will begin to conduct electricity instead. This causes circuit board failures.
Controlled impedance
FR4 does not offer uniform dielectric constant like high-speed board materials. As the frequency goes up the Dk varies. Dielectric constant tolerances for high-speed materials are less than 2%, whereas for FR4 it is up to 10%. Dk variations in FR4 impose challenges while maintaining impedance values. Hence, this material is not a preferred choice for controlled impedance boards.
How to choose FR4 material for PCB with the considerations?
Thickness of Sheet:
Basically, the thickness depends on your project what do you want to make; thinnest boards are widely used for printed circuit boards designed. Thin PC boards reduce stress. Ideally, we require Fr4 thickness almost from 1 to 3 inches.
Impedance matching
In electrical and electronic equipment, impedance or frequency matching is very important for low-frequency or high-frequency printed circuit boards. Pay more attention to those points would help the boards to derive and run safely. It also can tell us about the capacitance in multi-sided boards.
Spacing
During the designing of Fr4 printed circuit boards, space-saving is a very important factor. For USB connectors and Bluetooth accessories, spacing is very important. Mostly we used the thinnest boards for designing.
Flexibility
The thinner board is more flexible than the thicker. Most manufacture used thin boards as compared to thick ones due to their flexibility. While using Fr4, if the substrate used is very thin and the area or dimensions of Fr4 PCB is more it would be a great risk. In electrical and electronic devices thin Fr4 PC boards having the ability to reduce stress. Thin boards are more flexible and more vulnerable to heat. During soldering, it can be bending to make a desirable angle.
Industry Category











