how to read a circuit board
By:PCBBUY 12/15/2023 07:09
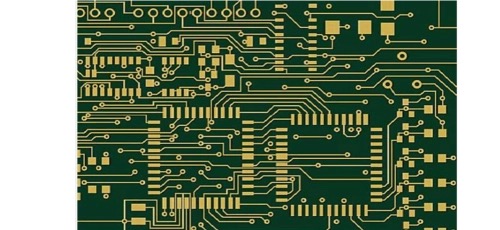
Circuit boards, also known as printed circuit boards (PCBs), are an essential component in electronic devices, facilitating the connection of electronic components and enabling circuit functionality. However, for beginners, understanding how to read a circuit board can be a challenging task. This article aims to comprehensively detail how to read a circuit board, including foundational knowledge, component identification, circuit analysis methods, and practical tips to aid readers in better understanding circuit boards.
1. Foundational Knowledge
-
Types of Circuit Boards: Understanding various types like single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards along with their characteristics and applications.
-
Component Packaging: Familiarity with common electronic component packaging such as DIP, SOP, QFP, aiding in component identification on the board.
-
Board Size and Thickness: Awareness of circuit board size and thickness specifications for selecting suitable boards in practical applications.
2. Component Identification
-
Resistors: Identification of resistance values typically represented by color bands, decoding resistance values from color sequences.
-
Capacitors: Recognizing different capacitor packages like through-hole or surface-mount, understanding units and capacitance values (uF, pF).
-
Inductors: Identification of inductance values usually displayed through color bands or numerical markings, noting units and value representation (uH, mH).
-
Semiconductor Devices: Understanding devices like diodes, transistors, MOSFETs, focusing on pin configurations and functionalities.
-
Integrated Circuits (ICs): Recognizing various IC types, understanding model numbers, pin layouts, and operational principles.
3. Circuit Analysis Methods
-
Signal Flow: Tracing signal paths on the board from input to output, comprehending circuit functionalities and operation.
-
Power and Ground Lines: Identifying power and ground lines, understanding power supply methods and voltage levels.
-
Critical Nodes: Observing critical nodes like amplifiers, filters, regulators, comprehending their roles within the circuit.
-
Interconnections and Interfaces: Analyzing the board's connections with other boards or devices, understanding interfaces, connectors, and their functions.
4. Practical Tips
-
Use of Magnification: Utilizing magnification tools when examining small or densely packed circuit boards for better detail observation.
-
Reference Documentation: Referring to circuit schematics, layout diagrams, and related documents for a deeper understanding of the board's functionality and design.
-
Testing Equipment Usage: Employing tools like multimeters, oscilloscopes for testing and analyzing components and circuits on the board.
-
Seeking Expert Advice: Consulting professionals when encountering complex or challenging issues for guidance and assistance.
5. Precautions
-
Safety First: Adhering to safety protocols while examining circuit boards to prevent electrical hazards or other risks.
-
Careful Observation: Being attentive while analyzing components and circuits as they are often intricate and densely arranged.
-
Continuous Learning: Acknowledging the ever-evolving nature of electronics, maintaining continuous learning to adapt to new technologies and applications.
By reading this article, readers should have grasped fundamental knowledge and methods for reading circuit boards. Through continuous practice and learning, individuals can progressively enhance their skills to better comprehend and analyze circuit boards.
Industry Category











