PCB Countersink Guide for Design Engineers and PCB Buyers
By:PCBBUY 11/24/2025 13:50
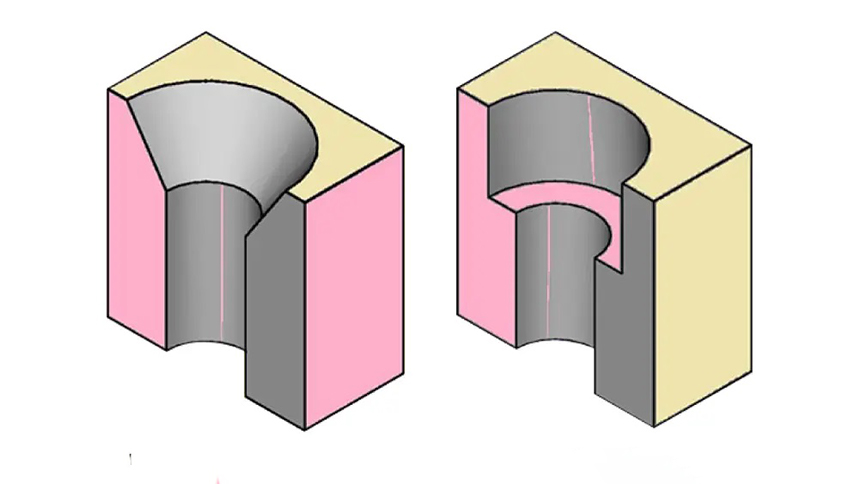
Countersink hole can also be necessary when creating a PCB, which is supposed to accept mechanical components, particularly screws or metal enclosures, without any trouble. It allows a screw head to be placed flat on the PCB surface enhance product appearance and structure stability.
Nowadays, counter sink machining is an extremely popular method in the consumer electronics and auto parts spheres, as well as in industry overall, in which PCB boards must be fastened into a container.
We will discuss what a PCB countersink is, how it works, the important design considerations, and the reasons why PCBBUY is relied upon to manufacture high precision countersink by global customers in this article..
What Is a PCB Countersink?
A PCB countersink is a conical cut made at the opening of a hole, typically used to accommodate flat-head screws. This allows the screw to be level with the PCB surface instead of protruding above it.
Countersinks are usually specified with:
-
Hole diameter
-
Countersink diameter
-
Countersink angle (commonly 82°, 90°, or 100°)
-
Depth or “with screw flush requirement”
-
Single-sided or double-sided machining
Countersink is often confused with counterbore, but they serve different purposes:
-
Countersink = conical shape for flat-head screws
-
Counterbore = cylindrical flat-bottom pocket for socket-head screws
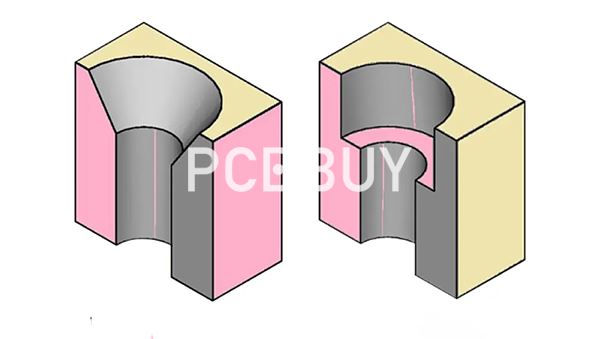
Why Do PCB Designers Use Countersink Holes?
There are several practical reasons:
1. Flush Screw Installation
A flush screw head prevents interference with other mechanical parts and improves safety.
2. Better Aesthetic Appearance
Many high-end consumer products require a clean, flat surface.
3. Strengthened Mechanical Assembly
Properly machined countersinks ensure screws sit firmly, reducing stress on the PCB.
4. Compatibility With Metal Enclosures
Countersinks help align the PCB precisely inside aluminum or steel housings.
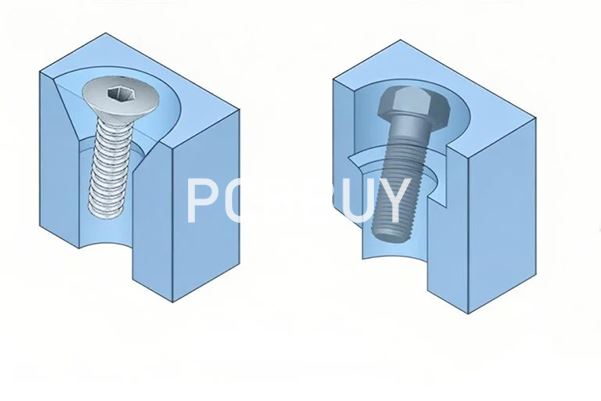
How PCB Countersinks Are Manufactured?
Creating a precise countersink requires controlled CNC drilling and milling. At PCBBUY, the process is carefully engineered:
• CNC Drilling
The base hole (PTH or NPTH) is drilled first based on the specified diameter.
• CNC Milling or Chamfer Tooling
A conical milling tool creates the required countersink angle and depth.
• Tolerance Calibration
Angle, position, and depth are verified to match the engineering file.
• Inspection & Fit Test
A real screw is inserted to confirm the flush level and mechanical fit.
Countersinks on multilayer PCB require additional engineering review because the remaining copper and substrate thickness must not be compromised.
PCBBUY’s Manufacturing Capability for PCB Countersinks
As a professional PCB manufacturer serving global markets, PCBBUY delivers stable and accurate countersink machining for prototypes and mass production. Our key strengths include:
● High Precision CNC Equipment
-
Hole position accuracy: ±3 mil
-
Countersink depth control: ±0.1 mm
-
Supported angles: 82°, 90°, 100°
● Support for Both PTH & NPTH Countersink Holes
Whether the hole is plated or non-plated, our process ensures smooth walls and consistent angles.
● Experienced Engineering Team
Our engineers review every countersink request:
-
Board thickness
-
Drill chart
-
Screw type
-
Required depth
-
Avoiding exposure of inner copper layers
● Full DFM Assistance
If a designer is unsure about the required depth or angle, PCBBUY offers free DFM suggestions.
● Fast Lead Time
-
Prototype: 24–48 hours
-
Mass production: 5–7 working days
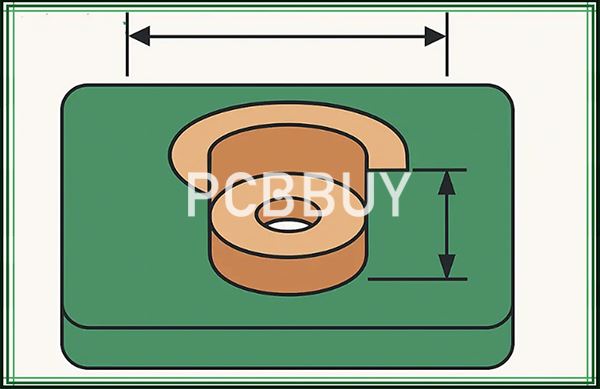
Design Guidelines for PCB Countersink Holes
To avoid production issues, here are practical design tips:
1. Provide Clear Specifications
Include:
-
Angle
-
Depth or “flush screw requirement”
-
Hole diameter
-
Single or double-sided machining
2. Check Minimum Board Thickness
The countersink depth must not weaken the PCB.
3. Avoid Copper Too Close to the Hole
Keep copper at least 0.3 mm away from the edge of the countersink area.
4. Use NPTH for Screw Holes When Possible
NPTH reduces risk of plating cracks during screw tightening.
5. Provide Screw Model (If Available)
This helps our engineers match the correct countersink geometry.
Applications of PCB Countersink Machining
You will typically find countersink holes in:
-
Smart home devices
-
Industrial control units
-
Automotive electronics
-
Communication equipment
-
Consumer electronics
-
Metal chassis assemblies
PCBBUY has supported thousands of global customers in these industries, handling high-precision countersink designs on FR4, aluminum PCB, rigid-flex PCB, and multilayer HDI boards.

Why Choose PCBBUY for PCB Countersink Projects?
Here’s why more overseas buyers prefer PCBBUY:
1. Professional Countersink Experience
We handle complex countersink geometries with tight tolerances.
2. Reliable Quality Control
3D measurement tools check angle, depth, diameter, and screw fit.
3. Engineer-to-Engineer Support
Our team communicates directly with your engineering department for DFM checks.
4. One-Stop PCB + Assembly
We provide PCB fabrication, components sourcing, and PCBA assembly in-house.
5. Global Shipping & Stable Lead Time
Orders are shipped quickly to the US, Europe, Australia, and Southeast Asia.
Conclusion
A well-designed PCB countersink improves mechanical fit, appearance, and functional performance. With the right engineering capability, it becomes a simple yet powerful design element in modern electronics.
If you’re developing a PCB that requires countersink machining, PCBBUY is fully equipped to support your prototype and mass-production needs with high precision and fast lead times.
Contact PCBBUY today for professional PCB countersink manufacturing and free DFM support.
FAQ
1. What is a PCB countersink?
A PCB countersink is a tapered cut applied to a hole so that a flat-head screw can sit flush with the board surface. It ensures smooth assembly, prevents screw protrusion, and improves mechanical stability.
2. When should I use a countersink instead of a counterbore?
Use a countersink for flat-head screws that require a conical seat.
Use a counterbore when you need a cylindrical pocket for socket-head screws.
The choice depends on screw type and mechanical fastening requirements.
3. Does countersinking affect PCB manufacturability?
Yes. Countersink depth, angle, and plating requirements must match the drill size and PCB thickness. Incorrect specifications may cause drill breakthrough or insufficient copper retention. PCBBUY performs DFM checks to confirm manufacturability before production.
4. What countersink angles are commonly supported?
Most PCB fabs—including PCBBUY—support 82°, 90°, and 100°. Custom angles are also possible but require engineering confirmation.
5. Can a countersink be applied to plated holes (PTH)?
Yes, but it must be handled carefully. Countersinking a plated hole may reduce plating thickness at the edge. In many mechanical designs, NPTH countersinks are preferred to avoid plating stress or cracking.
Industry Category











