A Comprehensive Guide of Flow Soldering vs Reflow Soldering
By:PCBBUY 10/28/2025 14:00
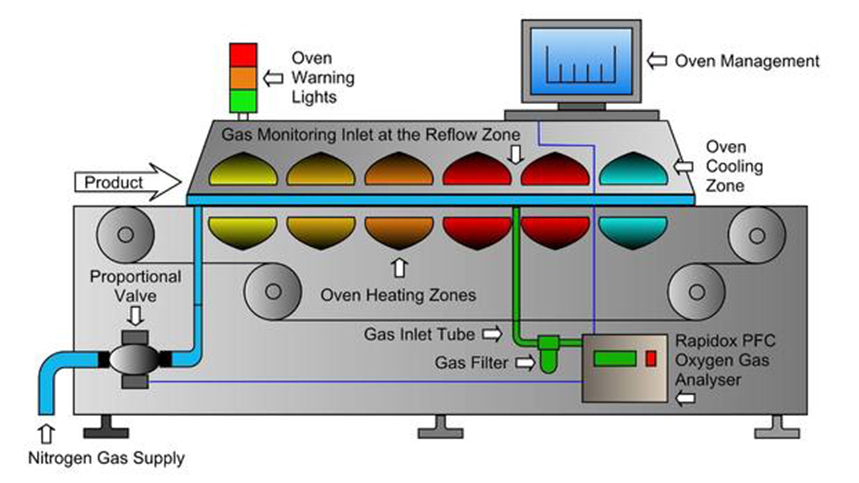
In regards to PCB assembly, it is important to know the dissimilarity between flow soldering and reflow soldering to produce high quality and reliable PCBs. Both methods have some applications, and advantages. In PCBBUY, the advanced reflow technology as well as flow soldering technology is used to provide the accuracy, uniformity and high quality of performance by all the production lines.
1. What Is Flow Soldering?
Flow soldering/wave soldering is a soldering process, mostly utilized to assemble through-hole components. With this technique, a flowing solder molten chassis is applied continuously under the PCB and connects component leads to the pads during one step.
Key Steps in Flow Soldering
-
Flux Application – A layer of flux is applied to remove oxides and improve solder wetting.
-
Preheating – The board is preheated to activate the flux and prevent thermal shock.
-
Solder Wave Contact – The PCB passes over a wave of molten solder, forming reliable joints.
-
Cooling – The assembly is gradually cooled to stabilize the solder joints.
At PCBBUY, our systems of automated soldering of the waves guarantee effective control of the temperature and the perfect solder waves. This reduces bridging, icicles and other prevalent defects of soldering ensuring seamless solder joints on high density boards.
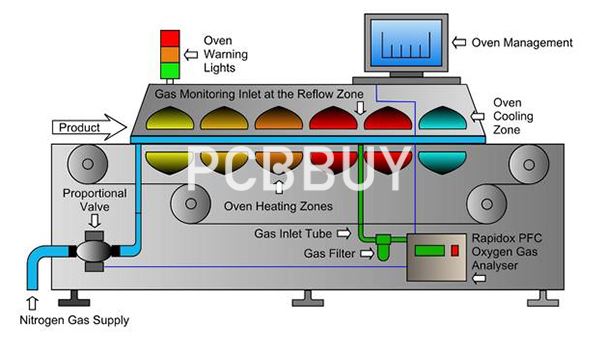
2. What Is Reflow Soldering?
Reflow soldering is typically used for Surface Mount Technology (SMT) components. Instead of a molten wave, this method relies on solder paste—a mixture of solder powder and flux—applied directly to the PCB pads before components are placed and heated.
Reflow Soldering Process Steps
-
Solder Paste Printing – Paste is deposited on the PCB pads via stencil printing.
-
Component Placement – SMT components are accurately positioned by automated pick-and-place machines.
-
Preheating – The assembly is gradually warmed to activate the flux.
-
Reflow Zone – The temperature rises above solder melting point, forming strong metallurgical bonds.
-
Cooling – Controlled cooling solidifies the joints for mechanical and thermal reliability.
At PCBBUY, our reflow ovens feature multi-zone temperature profiling for different PCB materials and solder pastes. This ensures uniform heating, precise thermal control, and void-free solder joints, meeting international standards like IPC-A-610 Class 2 and Class 3.

3. Flow Soldering vs Reflow Soldering: A Detailed Comparison
|
Parameter |
Flow Soldering |
Reflow Soldering |
|
Component Type |
Through-hole |
Surface mount |
|
Solder Type |
Molten wave |
Solder paste |
|
Temperature Control |
Single-stage heating |
Multi-zone thermal profile |
|
Automation Level |
Moderate |
High |
|
Best Suited For |
Double-sided or mixed-technology PCBs |
High-density SMT boards |
|
Common Defects |
Bridging, icicles, cold joints |
Tombstoning, voids, insufficient wetting |
Both processes have their advantages. Flow soldering is ideal for robust, larger components that need strong mechanical connections. Reflow soldering, on the other hand, excels in miniaturized assemblies with tight pad spacing and fine-pitch ICs.
4. How PCBBUY Ensures Excellence in Both Soldering Methods
At PCBBUY, we understand that every PCB project is unique. Our engineers carefully evaluate the design requirements to determine the optimal soldering method—flow soldering vs reflow soldering—based on component type, board layout, and performance expectations.
Our Manufacturing Advantages:
-
Advanced Soldering Equipment: High-precision reflow ovens and wave soldering lines for small to mass-scale production.
-
Automated Quality Inspection: AOI and X-ray inspection to detect hidden defects and ensure IPC-compliant solder joints.
-
Custom Thermal Profiling: Tailored temperature profiles for leaded and lead-free processes.
-
Material Expertise: Compatibility with FR4, Rogers, and aluminum substrates.
-
Consistent Quality: Every board undergoes rigorous in-process control, ensuring consistent solder joint quality and reliability.

5. Choosing Between Flow and Reflow Soldering for Your Project
If your PCB design includes only SMT components, reflow soldering is the best choice for accuracy and compactness. For through-hole or mixed-technology boards, combining reflow soldering for SMT and flow soldering for through-hole yields the most reliable results.
At PCBBUY, our integrated assembly lines support both processes seamlessly, allowing customers to benefit from hybrid PCBA manufacturing solutions—optimized for cost, performance, and turnaround time.
6. Conclusion: PCBBUY’s Commitment to Soldering Excellence
Whether your project requires flow soldering or reflow soldering, PCBBUY guarantees top-tier quality, reliability, and precision. Our expertise in SMT and THT assembly, combined with world-class equipment and IPC-compliant standards, ensures your PCBAs meet the highest expectations.
Partner with PCBBUY for advanced PCB and PCBA services where engineering precision meets manufacturing excellence.

FAQ: Flow Soldering vs Reflow Soldering
Q1: What is the main difference between flow soldering vs reflow soldering?
Flow soldering uses a molten solder wave for through-hole components, while reflow soldering uses solder paste for surface-mount components.
Q2: Which process is better for multilayer boards?
Reflow soldering is generally preferred for multilayer and high-density PCBs due to its controlled heating profile.
Q3: Does PCBBUY offer both flow and reflow soldering services?
Yes. PCBBUY provides full SMT and THT assembly solutions, including both flow and reflow soldering processes.
Q4: How does PCBBUY control soldering quality?
We use AOI inspection, X-ray testing, and thermal profiling to ensure every solder joint meets IPC standards.
Industry Category











